Three is a crowd
- PMID: 25169575
- PMCID: PMC4188853
- DOI: 10.1007/s12471-014-0586-0
Three is a crowd
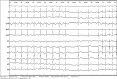
Figures

References
-
- Priori SG, Wilde AA, Horie M, et al. HRS/EHRA/APHRS Expert Consensus Statement on the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Inherited Primary Arrhythmia Syndromes. Expert Consensus Statement on Inherited Primary Arrhythmia Syndromes. Heart Rhythm. 2013:e75-e106 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

