Clinical and radiographic outcomes at 2 years and the effect of tocilizumab discontinuation following sustained remission in the second and third year of the ACT-RAY study
- PMID: 25169728
- PMCID: PMC4283697
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205752
Clinical and radiographic outcomes at 2 years and the effect of tocilizumab discontinuation following sustained remission in the second and third year of the ACT-RAY study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab (TCZ) plus methotrexate/placebo (MTX/PBO) over 2 years and the course of disease activity in patients who discontinued TCZ due to sustained remission.
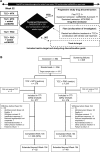
Methods: ACT-RAY was a double-blind 3-year trial. Patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite MTX were randomised to add TCZ to ongoing MTX (add-on strategy) or switch to TCZ plus PBO (switch strategy). Using a treat-to-target approach, open-label conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs), other than MTX, were added from week 24 if Disease Activity Score in 28 joints based on erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) >3.2. Between weeks 52 and 104, patients in sustained clinical remission (DAS28-ESR <2.6 at two consecutive visits 12 weeks apart) discontinued TCZ and were assessed every 4 weeks for 1 year. If sustained remission was maintained, added csDMARDs, then MTX/PBO, were discontinued.
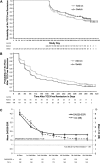
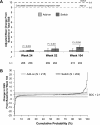
Results: Of the 556 randomised patients, 76% completed year 2. Of patients entering year 2, 50.4% discontinued TCZ after achieving sustained remission and 5.9% achieved drug-free remission. Most patients who discontinued TCZ (84.0%) had a subsequent flare, but responded well to TCZ reintroduction. Despite many patients temporarily stopping TCZ, radiographic progression was minimal, with differences favouring add-on treatment. Rates of serious adverse events and serious infections per 100 patient-years were 12.2 and 4.4 in add-on and 15.0 and 3.7 in switch patients. In patients with normal baseline values, alanine aminotransferase elevations >3×upper limit of normal were more frequent in add-on (14.3%) versus switch patients (5.4%).
Conclusions: Treat-to-target strategies could be successfully implemented with TCZ to achieve sustained remission, after which TCZ was stopped. Biologic-free remission was maintained for about 3 months, but most patients eventually flared. TCZ restart led to rapid improvement.
Trial registration number: NCT00810199.
Keywords: DMARDs (biologic); Methotrexate; Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
References
-
- Allaart CF, Lems WF, Huizinga TW. The BeSt way of withdrawing biologic agents. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2013;31(4 Suppl 78):S14–18. - PubMed
-
- Saleem B, Keen H, Goeb V, et al. Patients with RA in remission on TNF blockers: When and in whom can TNF blocker therapy be stopped? Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1636–42. - PubMed
-
- Quinn MA, Conaghan PG, O'Connor PJ, et al. Very early treatment with infliximab in addition to methotrexate in early, poor-prognosis rheumatoid arthritis reduces magnetic resonance imaging evidence of synovitis and damage, with sustained benefit after infliximab withdrawal: Results from a twelve-month randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:27–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

