Rare case of omentum-wrapped abscess caused by a fish bone penetrating the terminal ileum
- PMID: 25170236
- PMCID: PMC4145790
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11456
Rare case of omentum-wrapped abscess caused by a fish bone penetrating the terminal ileum
Abstract
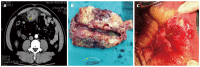
Accidentally ingested foreign bodies, for the most part, pass through the gastrointestinal tract, but can cause several complications. Perforation is rare, but can occur in any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal perforations due to foreign bodies are rarely diagnosed preoperatively as clinical symptoms are non-specific and they can mimic other abdominal conditions. We describe a case of a 48-year-old patient who was admitted to the emergency room because of severe abdominal pain of 5 d duration. A computed tomography scan showed an undefined liquid collection involving a linear image 35 mm in size, suggestive of a foreign body. On laparotomy, an abscess containing a fish bone was resected. As fish bone ingestion is usually not remembered by the patient, the diagnosis can be delayed. The preoperative diagnosis is frequently acute abdomen of unknown cause. A low threshold of suspicion along with a good clinical history and radiological studies are extremely important in order to make a correct diagnosis.
Keywords: Fish bone; Foreign body; Terminal ileum perforation.
Figures
References
-
- Puia IC, Puia VR, Andreescu A, Cristea PG. [Ascending colon perforation by ingested fruit stones] Chirurgia (Bucur) 2011;106:825–827. - PubMed
-
- Chiu JJ, Chen TL, Zhan YL. Perforation of the transverse colon by a fish bone: a case report. J Emerg Med. 2009;36:345–347. - PubMed
-
- Sierra-Solís A. [Bowel perforations due to fish bones: rare and curious] Semergen. 2013;39:117–118. - PubMed
-
- Eisen GM, Baron TH, Dominitz JA, Faigel DO, Goldstein JL, Johanson JF, Mallery JS, Raddawi HM, Vargo JJ, Waring JP, et al. Guideline for the management of ingested foreign bodies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;55:802–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

