Preparation, characterization, and in vitro osteoblast functions of a nano-hydroxyapatite/polyetheretherketone biocomposite as orthopedic implant material
- PMID: 25170265
- PMCID: PMC4145828
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S67358
Preparation, characterization, and in vitro osteoblast functions of a nano-hydroxyapatite/polyetheretherketone biocomposite as orthopedic implant material
Abstract
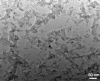
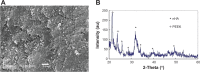
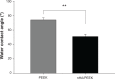
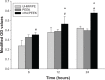
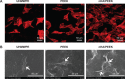
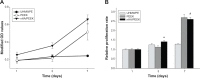
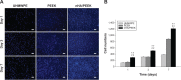
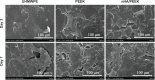
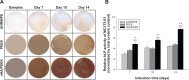
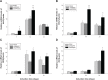
A bioactive composite was prepared by incorporating 40 wt% nano-hydroxyapatite (nHA) into polyetheretherketone (PEEK) through a process of compounding, injection, and molding. The mechanical and surface properties of the nHA/PEEK composite were characterized, and the in vitro osteoblast functions in the composite were investigated. The mechanical properties (elastic modulus and compressive strength) of the nHA/PEEK composite increased significantly, while the tensile strength decreased slightly as compared with PEEK. Further, the addition of nHA into PEEK increased the surface roughness and hydrophilicity of the nHA/PEEK composite. In cell tests, compared with PEEK and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene, it was found that the nHA/PEEK composite could promote the functions of MC3T3-E1 cells, including cell attachment, spreading, proliferation, alkaline phosphatase activity, calcium nodule formation, and expression of osteogenic differentiation-related genes. Incorporation of nHA into PEEK greatly improved the bioperformance of PEEK. The nHA/PEEK composite might be a promising orthopedic implant material.
Keywords: biocomposite; nano-hydroxyapatite; orthopedic implant material; osteoblast functions; polyetheretherketone.
Figures

References
-
- McMahon RE, Wang L, Skoracki R, Mathur AB. Development of nanomaterials for bone repair and regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(2):387–397. - PubMed
-
- Lee JS, Baek SD, Venkatesan J, et al. In vivo study of chitosan-natural nano hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;67:360–366. - PubMed
-
- Roeder RK, Converse GL, Kane RJ, Yue W. Hydroxyapatite-reinforced polymer biocomposites for synthetic bone substitutes. JOM. 2008;60(3):38–45.
-
- Zong C, Qian X, Tang Z, et al. Biocompatibility and bone-repairing effects: comparison between porous poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid and nano-hydroxyapatite/poly(lactic acid) scaffolds. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(6):1091–1104. - PubMed
-
- Asti A, Gioglio L. Natural and synthetic biodegradable polymers: different scaffolds for cell expansion and tissue formation. Int J Artif Organs. 2014;37(3):187–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

