Noninvasive risk stratification of lung adenocarcinoma using quantitative computed tomography
- PMID: 25170645
- PMCID: PMC4254143
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000319
Noninvasive risk stratification of lung adenocarcinoma using quantitative computed tomography
Abstract
Introduction: Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States and worldwide. Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer and encompasses lesions with widely variable clinical outcomes. In the absence of noninvasive risk stratification, individualized patient management remains challenging. Consequently a subgroup of pulmonary nodules of the lung adenocarcinoma spectrum is likely treated more aggressively than necessary.
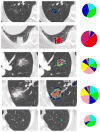
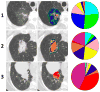
Methods: Consecutive patients with surgically resected pulmonary nodules of the lung adenocarcinoma spectrum (lesion size ≤3 cm, 2006-2009) and available presurgical high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) imaging were identified at Mayo Clinic Rochester. All cases were classified using an unbiased Computer-Aided Nodule Assessment and Risk Yield (CANARY) approach based on the quantification of presurgical HRCT characteristics. CANARY-based classification was independently correlated to postsurgical progression-free survival.
Results: CANARY analysis of 264 consecutive patients identified three distinct subgroups. Independent comparisons of 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) between these subgroups demonstrated statistically significant differences in 5-year DFS, 100%, 72.7%, and 51.4%, respectively (p = 0.0005).
Conclusions: Noninvasive CANARY-based risk stratification identifies subgroups of patients with pulmonary nodules of the adenocarcinoma spectrum characterized by distinct clinical outcomes. This technique may ultimately improve the current expert opinion-based approach to the management of these lesions by facilitating individualized patient management.
Figures

Comment in
-
The bell tolls for indeterminant lung nodules: computer-aided nodule assessment and risk yield (CANARY) has the wrong tune.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Aug;8(8):E836-7. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.07.85. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 27618999 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Society AC. Cancer Facts and Figures 2014. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2014.
-
- Moyer VA. Screening for lung cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Annals of internal medicine. 2014 - PubMed
-
- Jaklitsch MT, Jacobson FL, Austin JH, et al. The American Association for Thoracic Surgery guidelines for lung cancer screening using low-dose computed tomography scans for lung cancer survivors and other high-risk groups. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2012;144:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

