The RADAR study: week 48 safety and efficacy of RAltegravir combined with boosted DARunavir compared to tenofovir/emtricitabine combined with boosted darunavir in antiretroviral-naive patients. Impact on bone health
- PMID: 25170938
- PMCID: PMC4149560
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106221
The RADAR study: week 48 safety and efficacy of RAltegravir combined with boosted DARunavir compared to tenofovir/emtricitabine combined with boosted darunavir in antiretroviral-naive patients. Impact on bone health
Abstract
Background: NRTI-sparing regimens may avoid long-term mitochondrial, bone and renal toxicities and maintain viral suppression.
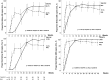
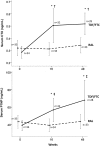
Methods: In the RADAR study, 85 antiretroviral-naïve HIV-infected patients were randomized to receive either raltegravir (RAL) (n = 42) or tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) (n = 43), each with ritonavir-boosted darunavir (DRV/r). Virologic efficacy was assessed at weeks 24 and 48. Bone mineral density (BMD) was assessed by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan at baseline and week 48, and bone turnover markers (BTM) assessed at weeks 0, 16 and 48.
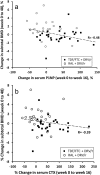
Results: Using an intention-to-treat analysis, 62.5% of RAL subjects and 83.7% of TDF/FTC subjects were responders (VL<48 copies/mL) at week 48 (p = 0.045; chi-square test). The proportions of patients achieving VL<200 copies/mL were similar: 72.5% and 86.0% (p = 0.175). Premature treatment discontinuation was the main cause for failure. No treatment-emergent resistance was observed. Changes from baseline in RAL vs. TDF/FTC for CD4+ (+199 vs. +216 cells/µL, p = 0.63), total cholesterol/HDL (-0.25 vs. -0.71 mg/dL (p = 0.270), and eGFR (-4.4 vs. -7.9 ml/min, p = 0.44) were comparable between groups. Changes in subtotal BMD to week 48 were: +9.2 with RAL vs. -7 g/cm2 with TDF/FTC (p = 0.002). Mean CTX changes were +0.04 vs. +0.24 ng/mL (p = 0.001), and mean P1NP changes were +3.59 vs. +30.09 ng/mL (p = 0.023). BTM changes at week 16 predicted change in BMD by week 48 (R = -0.394, p = 0.003 for CTX; and R = -0.477, p<0.001 for P1NP).
Conclusion: The NRTI-sparing regimen RAL+DRV/r did not achieve similar week 48 virologic efficacy compared with TDF/FTC+DRV/r, but was better with regard to markers of bone health.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT 00677300.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00677300.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bedimo R, Maalouf NM, Zhang S, Drechsler H, Tebas P (2012) Osteoporotic fracture risk associated with cumulative exposure to tenofovir and other antiretroviral agents. AIDS 26: 825–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

