Two rare AKAP9 variants are associated with Alzheimer's disease in African Americans
- PMID: 25172201
- PMCID: PMC4253055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2014.06.010
Two rare AKAP9 variants are associated with Alzheimer's disease in African Americans
Abstract
Background: Less is known about the genetic basis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in African Americans (AAs) than in non-Hispanic whites.
Methods: Whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed on seven AA AD cases. Disease association with potentially AD-related variants from WES was assessed in an AA discovery cohort of 422 cases and 394 controls. Replication was sought in an AA sample of 1037 cases and 1869 controls from the Alzheimer Disease Genetics Consortium (ADGC).
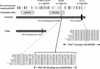
Results: Forty-four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from WES passed filtering criteria and were successfully genotyped. Nominally significant (P < .05) association to AD was observed with two African-descent specific AKAP9 SNPs in tight linkage disequilibrium: rs144662445 (P = .014) and rs149979685 (P = .037). These associations were replicated in the ADGC sample (rs144662445: P = .0022, odds ratio [OR] = 2.75; rs149979685: P = .0022, OR = 3.61).
Conclusions: Because AKAP9 was not previously linked to AD risk, this study indicates a potential new disease mechanism.
Keywords: AKAP9; African American; Genetic association; Late-onset Alzheimer's disease; Rare variant; Whole-exome sequencing.
Copyright © 2014 The Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this paper have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures


References
-
- Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, George-Hyslop PH, Pericak-Vance MA, Joo SH, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–1472. - PubMed
-
- Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, Hyman B, Kukull WA, Mayeux R, et al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype, Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. Jama. 1997;278:1349–1356. - PubMed
-
- Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, Campion D, Sleegers K, Hiltunen M, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1094–1099. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC2 AG036528/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041718/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG009029/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036650/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019085/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026390/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024151/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048927/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037212/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022018/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030653/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD000546/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

