Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching reveals regulation and distribution of connexin36 gap junction coupling within mouse islets of Langerhans
- PMID: 25172942
- PMCID: PMC4287745
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.276733
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching reveals regulation and distribution of connexin36 gap junction coupling within mouse islets of Langerhans
Erratum in
-
Corrigenda.J Physiol. 2015 Jul 15;593(14):3223. doi: 10.1113/JP270942. Epub 2015 Jun 19. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26176422 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
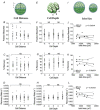
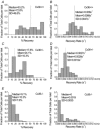
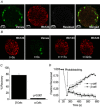
The pancreatic islets are central to the maintenance of glucose homeostasis through insulin secretion. Glucose‐stimulated insulin secretion is tightly linked to electrical activity in β cells within the islet. Gap junctions, composed of connexin36 (Cx36), form intercellular channels between β cells, synchronizing electrical activity and insulin secretion. Loss of gap junction coupling leads to altered insulin secretion dynamics and disrupted glucose homeostasis. Gap junction coupling is known to be disrupted in mouse models of pre‐diabetes. Although approaches to measure gap junction coupling have been devised, they either lack cell specificity, suitable quantification of coupling or spatial resolution, or are invasive. The purpose of this study was to develop fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) as a technique to accurately and robustly measure gap junction coupling in the islet. The cationic dye Rhodamine 123 was used with FRAP to quantify dye diffusion between islet β cells as a measure of Cx36 gap junction coupling. Measurements in islets with reduced Cx36 verified the accuracy of this technique in distinguishing between distinct levels of gap junction coupling. Analysis of individual cells revealed that the distribution of coupling across the islet is highly heterogeneous. Analysis of several modulators of gap junction coupling revealed glucose‐ and cAMP‐dependent modulation of gap junction coupling in islets. Finally, FRAP was used to determine cell population specific coupling, where no functional gap junction coupling was observed between α cells and β cells in the islet. The results of this study show FRAP to be a robust technique which provides the cellular resolution to quantify the distribution and regulation of Cx36 gap junction coupling in specific cell populations within the islet. Future studies utilizing this technique may elucidate the role of gap junction coupling in the progression of diabetes and identify mechanisms of gap junction regulation for potential therapies.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Low Level Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Decrease Connexin36 Gap Junction Coupling in Mouse and Human Islets through Nitric Oxide-mediated Protein Kinase Cδ.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 12;291(7):3184-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.679506. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26668311 Free PMC article.
-
Exendin-4 overcomes cytokine-induced decreases in gap junction coupling via protein kinase A and Epac2 in mouse and human islets.J Physiol. 2019 Jan;597(2):431-447. doi: 10.1113/JP276106. Epub 2018 Nov 29. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30412665 Free PMC article.
-
Restoring connexin-36 function in diabetogenic environments precludes mouse and human islet dysfunction.J Physiol. 2023 Sep;601(18):4053-4072. doi: 10.1113/JP282114. Epub 2023 Aug 14. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37578890 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of connexins in pancreatic islet function and diabetes.FEBS Lett. 2014 Apr 17;588(8):1278-87. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.02.035. Epub 2014 Feb 28. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24583073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexins and microRNAs: Interlinked players in regulating islet function?Islets. 2017 Sep 3;9(5):99-108. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2017.1331192. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Islets. 2017. PMID: 28686518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aligned ovine diaphragmatic myoblasts overexpressing human connexin-43 seeded on poly (L-lactic acid) scaffolds for potential use in cardiac regeneration.Cytotechnology. 2018 Apr;70(2):651-664. doi: 10.1007/s10616-017-0166-4. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Cytotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29143226 Free PMC article.
-
Islet architecture in adult mice is actively maintained by Robo2 expression in β cells.Dev Biol. 2024 Jan;505:122-129. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2023.11.003. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 37972678 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Dependent Decline in the Coordinated [Ca2+] and Insulin Secretory Dynamics in Human Pancreatic Islets.Diabetes. 2017 Sep;66(9):2436-2445. doi: 10.2337/db17-0137. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28588099 Free PMC article.
-
Low Level Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Decrease Connexin36 Gap Junction Coupling in Mouse and Human Islets through Nitric Oxide-mediated Protein Kinase Cδ.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 12;291(7):3184-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.679506. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26668311 Free PMC article.
-
New Understanding of β-Cell Heterogeneity and In Situ Islet Function.Diabetes. 2018 Apr;67(4):537-547. doi: 10.2337/dbi17-0040. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29559510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbaci M, Barberi-Heyob M, Blondel W, Guillemin F, Dideldon J. Advantages and limitations of commonly used methods to assay the molecular permeability of gap junctional intercellular communication. BioTechniques. 2008;45:33–62. - PubMed
-
- Allagnat F, Martin D, Condorelli DF, Waeber G, Haefliger J-A. Glucose represses connexin36 in insulin-secreting cells. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:5335–5344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

