Nucleus accumbens medium spiny neuron subtypes mediate depression-related outcomes to social defeat stress
- PMID: 25173629
- PMCID: PMC5534173
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.07.021
Nucleus accumbens medium spiny neuron subtypes mediate depression-related outcomes to social defeat stress
Abstract
Background: The nucleus accumbens is a critical mediator of depression-related outcomes to social defeat stress. Previous studies demonstrate distinct neuroplasticity adaptations in the two medium spiny neuron (MSN) subtypes, those enriched in dopamine receptor D1 versus dopamine receptor D2, in reward and reinforcement leading to opposing roles for these MSNs in these behaviors. However, the distinct roles of nucleus accumbens MSN subtypes, in depression, remain poorly understood.
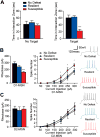
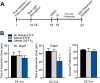
Methods: Using whole-cell patch clamp electrophysiology, we examined excitatory input to MSN subtypes and intrinsic excitability measures in D1-green fluorescent protein and D2-green fluorescent protein bacterial artificial chromosome transgenic mice that underwent chronic social defeat stress (CSDS). Optogenetic and pharmacogenetic approaches were used to bidirectionally alter firing of D1-MSNs or D2-MSNs after CSDS or before a subthreshold social defeat stress in D1-Cre or D2-Cre bacterial artificial chromosome transgenic mice.
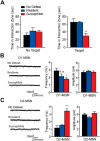
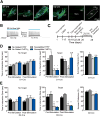
Results: We demonstrate that the frequency of excitatory synaptic input is decreased in D1-MSNs and increased in D2-MSNs in mice displaying depression-like behaviors after CSDS. Enhancing activity in D1-MSNs results in resilient behavioral outcomes, while inhibition of these MSNs induces depression-like outcomes after CSDS. Bidirectional modulation of D2-MSNs does not alter behavioral responses to CSDS; however, repeated activation of D2-MSNs in stress naïve mice induces social avoidance following subthreshold social defeat stress.
Conclusions: Our studies uncover novel functions of MSN subtypes in depression-like outcomes. Notably, bidirectional alteration of D1-MSN activity promotes opposite behavioral outcomes to chronic social stress. Therefore, targeting D1-MSN activity may provide novel treatment strategies for depression or other affective disorders.
Keywords: Depression; Medium spiny neurons; Nucleus accumbens; Optogenetics; Pharmacogenetics; Social defeat stress.
Copyright © 2015 Society of Biological Psychiatry. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stress and Cocaine Trigger Divergent and Cell Type-Specific Regulation of Synaptic Transmission at Single Spines in Nucleus Accumbens.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Jun 1;79(11):898-905. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.05.022. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26164802 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Slc6a15 in Nucleus Accumbens D2-Neurons Underlies Stress Susceptibility.J Neurosci. 2017 Jul 5;37(27):6527-6538. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3250-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jun 2. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28576941 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Type-Specific Epigenetic Editing at the Fosb Gene Controls Susceptibility to Social Defeat Stress.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Jan;43(2):272-284. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.88. Epub 2017 May 2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28462942 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role for Nucleus Accumbens Medium Spiny Neuron Subtypes in Depression.Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Apr 15;81(8):645-653. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Biol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27871668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Licking microstructure in response to novel rewards, reward devaluation and dopamine antagonists: Possible role of D1 and D2 medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024 Oct;165:105861. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105861. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024. PMID: 39159734 Review.
Cited by
-
Mono-methylation of lysine 27 at histone 3 confers lifelong susceptibility to stress.Neuron. 2024 Sep 4;112(17):2973-2989.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.06.006. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Neuron. 2024. PMID: 38959894
-
5-HT release in nucleus accumbens rescues social deficits in mouse autism model.Nature. 2018 Aug;560(7720):589-594. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0416-4. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30089910 Free PMC article.
-
Ventral Pallidum Is the Primary Target for Accumbens D1 Projections Driving Cocaine Seeking.J Neurosci. 2019 Mar 13;39(11):2041-2051. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2822-18.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 8. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30622165 Free PMC article.
-
Matcha Tea Powder's Antidepressant-like Effect through the Activation of the Dopaminergic System in Mice Is Dependent on Social Isolation Stress.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 22;15(3):581. doi: 10.3390/nu15030581. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36771286 Free PMC article.
-
Stress vulnerability promotes an alcohol-prone phenotype in a preclinical model of sustained depression.Addict Biol. 2020 Jan;25(1):e12701. doi: 10.1111/adb.12701. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Addict Biol. 2020. PMID: 30561063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berton O, McClung CA, Dileone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ, et al. Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science. 2006;311:864–868. - PubMed
-
- Krishnan V, Han MH, Graham DL, Berton O, Renthal W, Russo SJ, et al. Molecular adaptations underlying susceptibility and resistance to social defeat in brain reward regions. Cell. 2007;131:391–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

