Identification of cytochrome P450 enzymes critical for lung tumorigenesis by the tobacco-specific carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK): insights from a novel Cyp2abfgs-null mouse
- PMID: 25173884
- PMCID: PMC4216058
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgu182
Identification of cytochrome P450 enzymes critical for lung tumorigenesis by the tobacco-specific carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK): insights from a novel Cyp2abfgs-null mouse
Abstract
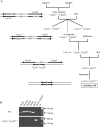
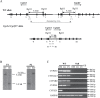
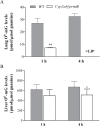
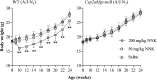
Cytochrome P450 (P450) enzymes encoded by the mouse Cyp2abfgs gene cluster are preferentially expressed in the respiratory tract. Previous studies have demonstrated that pulmonary P450-mediated bioactivation is necessary for lung tumorigenesis induced by the tobacco-specific lung procarcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK), and that CYP2A5 mediates a noteworthy fraction, but not all, of NNK bioactivation in the lung. The aim of this study was to determine whether other P450s encoded by the Cyp2abfgs gene cluster also play significant roles in NNK lung tumorigenesis. A novel Cyp2abfgs-null mouse was generated, in which all Cyp2a, 2b, 2g, 2f and 2s genes are deleted. The Cyp2abfgs-null mouse was viable, fertile and without discernible physiological abnormalities or compensatory increases in the expression of other P450s. NNK bioactivation in vitro and NNK-induced DNA adduction and lung tumorigenesis in vivo were determined for wild-type (WT) and Cyp2abfgs-null mice; the results were compared with previous findings from Cyp2a5-null mice. The Cyp2abfgs-null mice exhibited significantly lower rates of NNK bioactivation in lung and liver microsomes, compared with either WT or Cyp2a5-null mice. The levels of lung O(6)-methyl guanine DNA adduct were also substantially reduced in Cyp2abfgs-null mice, compared with either WT or Cyp2a5-null mice. Moreover, the Cyp2abfgs-null mice were largely resistant to NNK-induced lung tumorigenesis at both low (50mg/kg) and high (200mg/kg) NNK doses, in contrast to the WT or Cyp2a5-null mice. These results indicate for the first time that, collectively, the CYP2A, 2B, 2F, 2G, and 2S enzymes are indispensable for NNK-induced lung tumorigenesis.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of CYP2A13 in the bioactivation and lung tumorigenicity of the tobacco-specific lung procarcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone: in vivo studies using a CYP2A13-humanized mouse model.Carcinogenesis. 2014 Jan;35(1):131-7. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt269. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Carcinogenesis. 2014. PMID: 23917075 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CYP2A5 in the bioactivation of the lung carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone in mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Apr;341(1):233-41. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.190173. Epub 2012 Jan 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22262919 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of chemopreventive effects of 8-methoxypsoralen against 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced mouse lung adenomas.Carcinogenesis. 2005 Nov;26(11):1947-55. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi156. Epub 2005 Jun 15. Carcinogenesis. 2005. PMID: 15958517
-
Recent studies on mechanisms of bioactivation and detoxification of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK), a tobacco-specific lung carcinogen.Crit Rev Toxicol. 1996;26(2):163-81. doi: 10.3109/10408449609017929. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1996. PMID: 8688159 Review.
-
DNA adduct formation from tobacco-specific N-nitrosamines.Mutat Res. 1999 Mar 8;424(1-2):127-42. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(99)00014-7. Mutat Res. 1999. PMID: 10064856 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifunctional Activity-Based Protein Profiling of the Developing Lung.J Proteome Res. 2018 Aug 3;17(8):2623-2634. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00086. Epub 2018 Jul 18. J Proteome Res. 2018. PMID: 29972024 Free PMC article.
-
The epitranscriptomic writer ALKBH8 drives tolerance and protects mouse lungs from the environmental pollutant naphthalene.Epigenetics. 2020 Oct;15(10):1121-1138. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2020.1750213. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 32303148 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Transgene Location in the CYP2A13/2B6/2F1-transgenic Mouse Model using Optical Genome Mapping Technology.Drug Metab Dispos. 2023 Jan;51(1):46-53. doi: 10.1124/dmd.122.001090. Epub 2022 Oct 23. Drug Metab Dispos. 2023. PMID: 36273825 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Role of CYP2 Enzymes in the Atropselective Metabolism of Polychlorinated Biphenyls Using Liver Microsomes from Transgenic Mouse Models.Chem Res Toxicol. 2022 Dec 19;35(12):2310-2323. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.2c00276. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Chem Res Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36473170 Free PMC article.
-
Gene polymorphism of cytochrome P450 significantly affects lung cancer susceptibility.Cancer Med. 2019 Aug;8(10):4892-4905. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2367. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31264381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding X., et al. (2003). Human extrahepatic cytochromes P450: function in xenobiotic metabolism and tissue-selective chemical toxicity in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 43, 149–173 - PubMed
-
- Hecht S.S. (1998). Biochemistry, biology, and carcinogenicity of tobacco-specific N-nitrosamines. Chem. Res. Toxicol., 11, 559–603 - PubMed
-
- Peterson L.A., et al. (1991). O6-methylguanine is a critical determinant of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone tumorigenesis in A/J mouse lung. Cancer Res., 51, 5557–5564 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

