Etiologic heterogeneity among non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes: the InterLymph Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Subtypes Project
- PMID: 25174034
- PMCID: PMC4155467
- DOI: 10.1093/jncimonographs/lgu013
Etiologic heterogeneity among non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes: the InterLymph Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Subtypes Project
Abstract
Background: Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) comprises biologically and clinically heterogeneous subtypes. Previously, study size has limited the ability to compare and contrast the risk factor profiles among these heterogeneous subtypes.
Methods: We pooled individual-level data from 17 471 NHL cases and 23 096 controls in 20 case-control studies from the International Lymphoma Epidemiology Consortium (InterLymph). We estimated the associations, measured as odds ratios, between each of 11 NHL subtypes and self-reported medical history, family history of hematologic malignancy, lifestyle factors, and occupation. We then assessed the heterogeneity of associations by evaluating the variability (Q value) of the estimated odds ratios for a given exposure among subtypes. Finally, we organized the subtypes into a hierarchical tree to identify groups that had similar risk factor profiles. Statistical significance of tree partitions was estimated by permutation-based P values (P NODE).
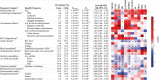
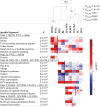
Results: Risks differed statistically significantly among NHL subtypes for medical history factors (autoimmune diseases, hepatitis C virus seropositivity, eczema, and blood transfusion), family history of leukemia and multiple myeloma, alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, and certain occupations, whereas generally homogeneous risks among subtypes were observed for family history of NHL, recreational sun exposure, hay fever, allergy, and socioeconomic status. Overall, the greatest difference in risk factors occurred between T-cell and B-cell lymphomas (P NODE < 1.0×10(-4)), with increased risks generally restricted to T-cell lymphomas for eczema, T-cell-activating autoimmune diseases, family history of multiple myeloma, and occupation as a painter. We further observed substantial heterogeneity among B-cell lymphomas (P NODE < 1.0×10(-4)). Increased risks for B-cell-activating autoimmune disease and hepatitis C virus seropositivity and decreased risks for alcohol consumption and occupation as a teacher generally were restricted to marginal zone lymphoma, Burkitt/Burkitt-like lymphoma/leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and/or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinemia.
Conclusions: Using a novel approach to investigate etiologic heterogeneity among NHL subtypes, we identified risk factors that were common among subtypes as well as risk factors that appeared to be distinct among individual or a few subtypes, suggesting both subtype-specific and shared underlying mechanisms. Further research is needed to test putative mechanisms, investigate other risk factors (eg, other infections, environmental exposures, and diet), and evaluate potential joint effects with genetic susceptibility.
Published by Oxford University Press 2014.
Figures




References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram L, Ervik M, et al. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. http://globocan.iarc.fr Accessed February 22, 2014
-
- Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW. eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2001
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 CA165923/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CP-ES-11027/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 CA102216/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000042/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA150037/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01 CA69669-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087014/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA150037/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA45614/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 ES011027/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA100555/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62006/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC-67008/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC067009/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N02-PC-71105/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA104682/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC-67010/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC067010/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL 1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA92153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA143947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC-65064/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- T32 HL007152/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC067008/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC014690/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- CA143947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA132153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA154643-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154643/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA062006/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050850/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000135/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA122663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC065064/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R13 CA159842 01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CO012400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA92153-S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA104682/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- CA165923/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA130805/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA51086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA033572/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03CA132153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097274/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA051086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149445/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100555/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA14690/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA045614/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA087014/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA97274/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CO-12400/CO/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA118444/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03CA125831/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA50850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CP-95618/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

