The impact of tumour size on the probability of synchronous metastasis and survival in renal cell carcinoma patients: a population-based study
- PMID: 25174263
- PMCID: PMC4159381
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2490-14-72
The impact of tumour size on the probability of synchronous metastasis and survival in renal cell carcinoma patients: a population-based study
Erratum in
-
Erratum: The impact of tumour size on the probability of synchronous metastasis and survival in renal cell carcinoma patients: a population-based study.BMC Urol. 2015 Feb 16;15:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-15-5. BMC Urol. 2015. PMID: 26065415 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The observed low metastatic potential and favorable survival of small incidentally detected renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) have been a part of the rationale for recommending partial nephrectomy as a first treatment option and active surveillance in selected patients. We examined the relationship between tumor size and the odds of synchronous metastases (SMs) (primary outcome) and disease specific survival (secondary outcome) in a nationwide RCC registry.
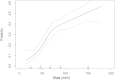
Methods: Retrospective study of the 794 RCC patients diagnosed in Iceland between 1971 and 2005. Histological material and TNM staging were reviewed centrally. The presence of SM and survival were recorded. Cubic spline analysis was used to assess relationship between tumor size and probability of SM. Univariate and multivariate statistics were used to estimate prognostic factors for SM and survival.
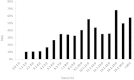
Results: The probability of SM increased in a non-linear fashion with increasing tumor size (11, 25, 35, and 50%) for patients with tumors of ≤4, 4.1-7.0, 7.1-10.0, and >10 cm, respectively. On multivariate analysis, tumor size was an independent prognostic factor for disease-specific survival (HR = 1.05, 95% CI 1.02-1.09, p < 0.001), but not for SM.
Conclusion: Tumor size affected the probability of disease-specific mortality but not SM, after correcting for TNM staging in multivariate analysis. This confirms the prognostic ability of the 2010 TNM staging system for renal cell cancer in the Icelandic population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Pulmonary resections for metastatic renal cell carcinoma in Iceland].Laeknabladid. 2008 May;94(5):377-81. Laeknabladid. 2008. PMID: 18460734 Icelandic.
-
Prognostic value of renal vein and inferior vena cava involvement in renal cell carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2009 Feb;55(2):452-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2008.07.053. Epub 2008 Aug 5. Eur Urol. 2009. PMID: 18692951
-
[Small renal cell carcinomas and synchronous metastases].Laeknabladid. 2012 Nov;98(11):585-9. doi: 10.17992/lbl.2012.11.461. Laeknabladid. 2012. PMID: 23232659 Icelandic.
-
Nephron-sparing surgery for renal cell carcinoma: clinicopathologic features predictive of patient outcome.Urology. 2003 Oct;62(4):641-6. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(03)00489-8. Urology. 2003. PMID: 14550434 Review.
-
Prognostic value of body mass index in patients undergoing nephrectomy for localized renal tumors.Urology. 2004 Jan;63(1):46-50. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2003.08.009. Urology. 2004. PMID: 14751346 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinicopathologica Epidemiological Characteristics and Change Tendencies of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Shanxi Province of China from 2005 to 2014.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 3;10(12):e0144246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144246. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26633179 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics, aetiology and implications for management of multiple primary renal tumours: a systematic review.Eur J Hum Genet. 2024 Aug;32(8):887-894. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01628-5. Epub 2024 May 27. Eur J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38802529 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of patients receiving systematic therapy for metachronous or synchronous metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a retrospective analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jul 15;19(1):688. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5900-1. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31307432 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum: The impact of tumour size on the probability of synchronous metastasis and survival in renal cell carcinoma patients: a population-based study.BMC Urol. 2015 Feb 16;15:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-15-5. BMC Urol. 2015. PMID: 26065415 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Risk Prediction Tool for Aggressive Tumors in Clinical T1 Stage Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Using Molecular Biomarkers.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Mar 8;17:371-377. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.03.005. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 30962867 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

