Oliguric acute kidney injury as a main symptom of bradycardia and arteriosclerosis resolved by pacemaker implantation: a case report
- PMID: 25175670
- PMCID: PMC4159969
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-289
Oliguric acute kidney injury as a main symptom of bradycardia and arteriosclerosis resolved by pacemaker implantation: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiovascular comorbidities regularly determine renal function. We report a case of acute kidney injury (Acute Kidney Injury Network stage 3) due to an intermittent third-degree atrioventricular block, which had not been diagnosed before.
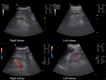
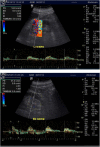
Case presentation: A 76-year-old Caucasian man with liver cirrhosis due to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and type-2 diabetes was cognitively impaired and had reduced vigilance presumably caused by hepatic encephalopathy and/or Alzheimer dementia. Within 2 years, two hospitalizations occurred for syncope attributed to orthostatic failure and hypovolemia. During the last hospitalization, oliguric acute kidney injury occurred. Sonography ruled out a post-renal cause. His renal resistive index was 1.0; his heart rate was below 50 beats per minute. After cessation of beta-blocker therapy, Holter electrocardiogram showed a new intermittent third-degree atrioventricular block with pauses for less than 3 seconds. Pacemaker insertion resolved his acute kidney injury, despite resumption of beta-blocker therapy. During four months of follow-up, syncope has not occurred, and vigilance was stable. However, his renal resistive index of 1.0 remained.
Conclusions: Here, typical neurologic symptoms of bradycardia were misclassified. Diagnostic work-up of oliguric acute kidney injury revealed intermittent third-degree heart block. The pathomechanism of acute kidney injury relates to relevant bradycardia and increased vascular stiffness attenuating arterial diastolic renal blood flow.
Figures

References
-
- Tonelli M, Muntner P, Lloyd A, Manns BJ, Klarenbach S, Pannu N, James MT, Hemmelgarn BR. Alberta Kidney Disease Network. Risk of coronary events in people with chronic kidney disease compared with those with diabetes: a population-level cohort study. Lancet. 2012;380:807–814. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60572-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davidavicius G, Chieffo A, Shannon J, Arioli F, Ielasi A, Mussardo M, Takagi K, Maisano F, Montorfano M, Godino C, Latib A, Colombo A. A high dose of adenosine to induce transient asystole for valvuloplasty in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI): is it a valid alternative to rapid pacing? A prospective pilot study. J Invasive Cardiol. 2011;23:467–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

