Water-based interventions for schistosomiasis control
- PMID: 25175875
- PMCID: PMC4153826
- DOI: 10.1179/2047773214Y.0000000149
Water-based interventions for schistosomiasis control
Abstract
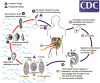
Mass drug administration with praziquantel is the mainstay of programs for the control of schistosomiasis morbidity. However, there is a growing recognition that treatment alone will not be sufficient for eventually effecting elimination and that additional measures will be required to interrupt transmission. In the absence of a safe and an effective vaccine for human schistosomiasis, the strategies to reduce infection levels will necessarily involve some interventions that affect the water-related stages of the schistosome life cycle: by reducing exposure to infectious water, by moderating availability of the intermediate snail host, or by decreasing contamination of water with egg-containing excreta. While much research on the importance of water on schistosomiasis has been performed, advances in these areas have perhaps languished with the ready availability of a cost-effective treatment. As some endemic areas near a shift to an elimination goal, a better understanding of water-based interventions that can be used alone or in concert with treatment will be needed. Reinvigoration of laboratory, field, and human behavioral aspects of this research now will ensure that the appropriate strategies are available by the time their implementation becomes necessary.
Keywords: Control,; Elimination,; Schistosomiasis,; Snail,; Transmission.; Water,.
Figures

References
-
- Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:411–25. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Schistosomiasis: Progress Report 2001–2011 and Strategic Plan 2012–2020 Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
