Vitamin E and D regulation of allergic asthma immunopathogenesis
- PMID: 25175918
- PMCID: PMC4254328
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.08.007
Vitamin E and D regulation of allergic asthma immunopathogenesis
Abstract
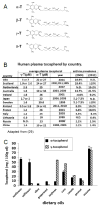
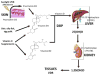
Asthma occurs as complex interactions of the environmental and genetics. Clinical studies and animal models of asthma indicate dietary factors such as vitamin E and vitamin D as protective for asthma risk. In this review, we discuss opposing regulatory functions of tocopherol isoforms of vitamin E and regulatory functions of vitamin D in asthma and how the variation in global prevalence of asthma may be explained, at least in part, by these dietary components.
Keywords: Animal models; Asthma; Human; Vitamin D; α-Tocopherol; γ-Tocopherol.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Martinez FD. Genes, environments, development and asthma: A reappraisal. Eur Respir J. 2007;29:179–184. - PubMed
-
- Vollmer WM, Osborne ML, Buist AS. 20-year trends in the prevalence of asthma and chronic airflow obstruction in an hmo. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:1079–1084. - PubMed
-
- Uauy R, Hoffman DR, Birch EE, Birch DG, Jameson DM, Tyson J. Safety and efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids in the nutrition of very low birth weight infants: Soy oil and marine oil supplementation of formula. J Pediatr. 1994;124:612–620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

