Recent progress in the development of anti-malarial quinolones
- PMID: 25176157
- PMCID: PMC4162983
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-339
Recent progress in the development of anti-malarial quinolones
Abstract
Available anti-malarial tools have over the ten-year period prior to 2012 dramatically reduced the number of fatalities due to malaria from one million to less than six-hundred and thirty thousand. Although fewer people now die from malaria, emerging resistance to the first-line anti-malarial drugs, namely artemisinins in combination with quinolines and arylmethanols, necessitates the urgent development of new anti-malarial drugs to curb the disease. The quinolones are a promising class of compounds, with some demonstrating potent in vitro activity against the malaria parasite. This review summarizes the progress made in the development of potential anti-malarial quinolones since 2008. The efficacy of these compounds against both asexual blood stages and other stages of the malaria parasite, the nature of putative targets, and a comparison of these properties with anti-malarial drugs currently in clinical use, are discussed.
Figures

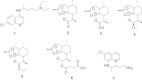
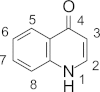



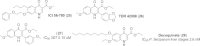

References
-
- WHO . World Malaria Report 2013. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- Guerra CA, Howes RE, Patil AP, Gething PW, Van Boeckel TP, Temperley WH, Kabaria CW, Tatem AJ, Manh BH, Elyazar RE, Baird JK, Snow RW, Hay SI. The international limits and population at risk of Plasmodium vivax transmission in 2009. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;4:e774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000774. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

