Increased behavioral responses to ethanol in Lmo3 knockout mice
- PMID: 25176312
- PMCID: PMC4442799
- DOI: 10.1111/gbb.12176
Increased behavioral responses to ethanol in Lmo3 knockout mice
Abstract
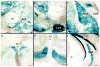
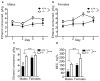
LIM-domain-only 3 (LMO3) is a transcriptional regulator involved in central nervous system development and neuroblastoma. Our previous studies implicated a potential role for LMO3 in regulating ethanol sensitivity and consumption. Here, we examined behavioral responses to ethanol in a line of Lmo3 null (Lmo3(Z) ) mice, utilizing the ethanol-induced loss-of-righting-reflex (LORR) test, two-bottle choice ethanol consumption and the drinking in the dark (DID) test, which models binge-like ethanol consumption. We found that Lmo3(Z) mice exhibited increased sedation time in response to ethanol in the LORR test and drank significantly more ethanol in the DID test compared with their wild-type counterparts, but showed no differences in two-bottle choice ethanol consumption. To explore where LMO3 may be acting in the brain to produce an ethanol phenotype, we also examined reporter gene (β-galactosidase) expression in heterozygous Lmo3(Z) mice and found strong expression in subcortical areas, particularly in those areas implicated in drug abuse, including the nucleus accumbens (Acb), cortex, hippocampus and amygdala. We also examined Lmo3 expression in the brains of wild-type mice who had undergone the DID test and found a negative correlation between Lmo3 expression in the Acb and the amount of ethanol consumed, consistent with the increased binge-like drinking observed in Lmo3(Z) mice. These results support a role for LMO3 in regulating behavioral responses to ethanol, potentially through its actions in the Acb.
Keywords: Binge drinking; LMO3; ethanol; sedation.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd and International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
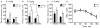

Similar articles
-
Regulation of anxiety-like behavior and Crhr1 expression in the basolateral amygdala by LMO3.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Jun;92:13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.03.016. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29609111 Free PMC article.
-
Lmo genes regulate behavioral responses to ethanol in Drosophila melanogaster and the mouse.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Sep;35(9):1600-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01506.x. Epub 2011 May 20. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21599714 Free PMC article.
-
Lmo3 deficiency in the mouse is associated with alterations in mood-related behaviors and a depression-biased amygdala transcriptome.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020 Jan;111:104480. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.104480. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31707294
-
The dorsal striatum expressing adenylyl cyclase-5 controls behavioral sensitivity of the righting reflex to high-dose ethanol.Brain Res. 2012 Dec 13;1489:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.016. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 23063718
-
Congenital brain serotonin deficiency leads to reduced ethanol sensitivity and increased ethanol consumption in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Feb;77:177-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24067926 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and Arealization of the Cerebral Cortex.Neuron. 2019 Sep 25;103(6):980-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.07.009. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31557462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using In Vitro Electrophysiology to Screen Medications: Accumbal Plasticity as an Engram of Alcohol Dependence.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016;126:441-65. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2016.02.018. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27055622 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms of Alcohol Neuroadaptation: Insights from Drosophila.J Exp Neurosci. 2018 Jun 4;12:1179069518779809. doi: 10.1177/1179069518779809. eCollection 2018. J Exp Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29899666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-Inducible, Beta in Alcohol-Drinking Behaviors.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Feb;40(2):263-72. doi: 10.1111/acer.12965. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 26842245 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of anxiety-like behavior and Crhr1 expression in the basolateral amygdala by LMO3.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Jun;92:13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.03.016. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29609111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoyama M, Ozaki T, Inuzuka H, Tomotsune D, Hirato J, Okamoto Y, Tokita H, Ohira M, Nakagawara A. LMO3 interacts with neuronal transcription factor, HEN2, and acts as an oncogene in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4587–4597. - PubMed
-
- Bulchand S, Subramanian L, Tole S. Dynamic spatiotemporal expression of LIM genes and cofactors in the embryonic and postnatal cerebral cortex. Dev Dyn. 2003;226:460–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

