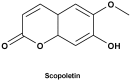
Scopoletin from Cirsium setidens Increases Melanin Synthesis via CREB Phosphorylation in B16F10 Cells
- PMID: 25177162
- PMCID: PMC4146632
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.4.307
Scopoletin from Cirsium setidens Increases Melanin Synthesis via CREB Phosphorylation in B16F10 Cells
Abstract
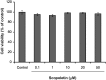
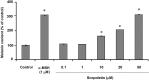
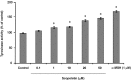
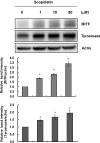
In this study, we isolated scopoletin from Cirsium setidens Nakai (Compositae) and tested its effects on melanogenesis. Scopoletin was not toxic to cells at concentrations less than 50 µM and increased melanin synthesis in a dose-dependent manner. As melanin synthesis increased, scopoletin stimulated the total tyrosinase activity, the rate-limiting enzyme of melanogenesis. In a cell-free system, however, scopoletin did not increase tyrosinase activity, indicating that scopoletin is not a direct activator of tyrosinase. Furthermore, Western blot analysis showed that scopoletin stimulated the production of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) and tyrosinase expression via cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. Based on these results, preclinical and clinical studies are needed to assess the use of scopoletin for the treatment of vitiligo.
Keywords: CREB; Cirsium setidens; MITF; Scopoletin; Tyrosinase.
Figures


References
-
- Hearing VJ, Tsukamoto K. Enzymatic control of pigmentation in mammals. FASEB J. 1991;5:2902–2909. - PubMed
-
- Pichler R, Sfetsos K, Badics B, Gutenbrunner S, Auböck J. Vitiligo patients present lower plasma levels of alpha-melanotropin immunoreactivities. Neuropeptides. 2006;40:177–183. - PubMed
-
- Lee WB, Kwon HC, Cho OR, Lee KC, Choi SU, Baek NI, Lee KR. Phytochemical constituents of Cirsium setidens Nakai and their cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines. Arch Pharm Res. 2002;25:628–635. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

