Paracrine effect of the bone morphogeneticprotein-2 at the experimental site on healing of the adjacent control site: a study in the rabbit calvarial defect model
- PMID: 25177519
- PMCID: PMC4148630
- DOI: 10.5051/jpis.2014.44.4.178
Paracrine effect of the bone morphogeneticprotein-2 at the experimental site on healing of the adjacent control site: a study in the rabbit calvarial defect model
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to assess the possible paracrine effect of bone morphogeneticprotein-2 (BMP-2) at the experimental site on the adjacent control site for validating a rabbit calvarial defect model as a means of verifying the effect of BMP-2.
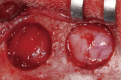
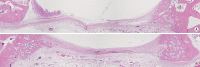
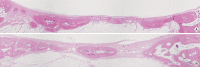
Methods: Sixteen rabbits were divided into two groups (n=8 in each) according to whether or not BMP-2 would be used. Two circular defects (8 mm in diameter) were created side by side, 2 mm apart, in the calvarium of all of the rabbits. In each animal, one of the defects was grafted with either BMP-2-loaded carrier or carrier material alone. The control defects adjacent to these grafted defects, designated CB (the nongrafted defect adjacent BMP-2-loaded carrier-grafted defect) and CC (the nongrafted defect adjacent to carrier only-grafted defect), respectively, were the focus of this study, and were filled only with a blood clot in all of the animals. Histologic observation and histomorphometric analysis were performed at 2 and 8 weeks (n=4 animals per point in time) after surgery.
Results: There was no noteworthy difference in the healing pattern, and no statistically significant differences in histomorphometric parameters such as the defect closure, new bone area, or total augmented area between the CC and CB groups.
Conclusions: The results of this study suggest that rabbit calvarial defects separated by a distance of 2 mm are suitable for evaluating the effects of BMP-2 and the control defect can be regarded not to be affected by BMP-2 applied defect.
Keywords: Animal experimentation; Bone morphogenetic protein 2; Bone regeneration; Research design.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Four-week histologic evaluation of grafted calvarial defects with adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy in rats.J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016 Aug;46(4):244-53. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2016.46.4.244. Epub 2016 Aug 30. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27588214 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Regeneration Potential of Biphasic Nanocalcium Phosphate with High Hydroxyapatite/Tricalcium Phosphate Ratios in Rabbit Calvarial Defects.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016 Mar-Apr;31(2):294-303. doi: 10.11607/jomi.4531. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016. PMID: 27004276
-
Bone healing with an in situ-formed bioresorbable polyethylene glycol hydrogel membrane in rabbit calvarial defects.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010 Mar;109(3):372-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.10.008. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010. PMID: 20060340
-
Osteogenic potential of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-9/absorbable collagen sponge (rhBMP-9/ACS) in rat critical size calvarial defects.Clin Oral Investig. 2017 Jun;21(5):1659-1665. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1963-4. Epub 2016 Oct 11. Clin Oral Investig. 2017. PMID: 27726024
-
Closure of rabbit calvarial critical-sized defects using protective composite allogeneic and alloplastic bone substitutes.J Craniofac Surg. 2006 Sep;17(5):926-34. doi: 10.1097/01.scs.0000230615.49270.d1. J Craniofac Surg. 2006. PMID: 17003622
Cited by
-
Enhanced Bone Formation by Rapidly Formed Bony Wall over the Bone Defect Using Dual Growth Factors.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023 Aug;20(5):767-778. doi: 10.1007/s13770-023-00534-z. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 37079199 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid bone regeneration by Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded on a hydroxyapatite carrier in the rabbit calvarial defect model.Biomater Res. 2015 Jul 16;19:17. doi: 10.1186/s40824-015-0039-x. eCollection 2015. Biomater Res. 2015. PMID: 26331086 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Enhanced Hydrophilic Titanium Dioxide-Coated Hydroxyapatite on Bone Regeneration in Rabbit Calvarial Defects.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 19;19(11):3640. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113640. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30463215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim JW, Choi KH, Yun JH, Jung UW, Kim CS, Choi SH, et al. Bone formation of block and particulated biphasic calcium phosphate lyophilized with Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 in rat calvarial defects. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112:298–306. - PubMed
-
- Kim JW, Jung IH, Lee KI, Jung UW, Kim CS, Choi SH, et al. Volumetric bone regenerative efficacy of biphasic calcium phosphate-collagen composite block loaded with rhBMP-2 in vertical bone augmentation model of a rabbit calvarium. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100:3304–3313. - PubMed
-
- Li P, Bai Y, Yin G, Pu X, Huang Z, Liao X, et al. Synergistic and sequential effects of BMP-2, bFGF and VEGF on osteogenic differentiation of rat osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Metab. 2013 Dec 05; [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00774-013-0538-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Freitas RM, Spin-Neto R, Junior EM, Pereira LA, Wikesjo UM, Susin C. Alveolar ridge and maxillary sinus augmentation using rhBMP-2: a systematic review. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013 Sep 17; [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/cid.12156. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

