Subsampled open-reference clustering creates consistent, comprehensive OTU definitions and scales to billions of sequences
- PMID: 25177538
- PMCID: PMC4145071
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.545
Subsampled open-reference clustering creates consistent, comprehensive OTU definitions and scales to billions of sequences
Abstract
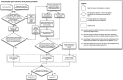
We present a performance-optimized algorithm, subsampled open-reference OTU picking, for assigning marker gene (e.g., 16S rRNA) sequences generated on next-generation sequencing platforms to operational taxonomic units (OTUs) for microbial community analysis. This algorithm provides benefits over de novo OTU picking (clustering can be performed largely in parallel, reducing runtime) and closed-reference OTU picking (all reads are clustered, not only those that match a reference database sequence with high similarity). Because more of our algorithm can be run in parallel relative to "classic" open-reference OTU picking, it makes open-reference OTU picking tractable on massive amplicon sequence data sets (though on smaller data sets, "classic" open-reference OTU clustering is often faster). We illustrate that here by applying it to the first 15,000 samples sequenced for the Earth Microbiome Project (1.3 billion V4 16S rRNA amplicons). To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest OTU picking run ever performed, and we estimate that our new algorithm runs in less than 1/5 the time than would be required of "classic" open reference OTU picking. We show that subsampled open-reference OTU picking yields results that are highly correlated with those generated by "classic" open-reference OTU picking through comparisons on three well-studied datasets. An implementation of this algorithm is provided in the popular QIIME software package, which uses uclust for read clustering. All analyses were performed using QIIME's uclust wrappers, though we provide details (aided by the open-source code in our GitHub repository) that will allow implementation of subsampled open-reference OTU picking independently of QIIME (e.g., in a compiled programming language, where runtimes should be further reduced). Our analyses should generalize to other implementations of these OTU picking algorithms. Finally, we present a comparison of parameter settings in QIIME's OTU picking workflows and make recommendations on settings for these free parameters to optimize runtime without reducing the quality of the results. These optimized parameters can vastly decrease the runtime of uclust-based OTU picking in QIIME.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Microbial ecology; Microbiome; OTU picking; Qiime.
Figures
References
-
- Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods. 2010;7(5):335–336. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cutting DR, Karger DR, Pedersen JO, Tukey JW. Scatter/gather: a cluster-based approach to browsing large document collections. Proceedings of the 15th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, SIGIR’92; New York, NY. 1992. pp. 318–329. - DOI
-
- DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2006;72(7):5069–5072. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03006-05. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources