Cerebral malaria: gamma-interferon redux
- PMID: 25177551
- PMCID: PMC4133756
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00113
Cerebral malaria: gamma-interferon redux
Abstract
There are two theories that seek to explain the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria, the mechanical obstruction hypothesis and the immunopathology hypothesis. Evidence consistent with both ideas has accumulated from studies of the human disease and experimental models. Thus, some combination of these concepts seems necessary to explain the very complex pattern of changes seen in cerebral malaria. The interactions between malaria parasites, erythrocytes, the cerebral microvascular endothelium, brain parenchymal cells, platelets and microparticles need to be considered. One factor that seems able to knit together much of this complexity is the cytokine interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). In this review we consider findings from the clinical disease, in vitro models and the murine counterpart of human cerebral malaria in order to evaluate the roles played by IFN-γ in the pathogenesis of this often fatal and debilitating condition.
Keywords: CD8+T lymphocyte; blood-brain barrier; cerebral malaria; immunopathology; interferon-gamma; kynurenine pathway; microparticles; platelets.
Figures

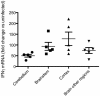
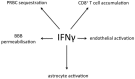
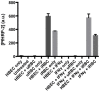
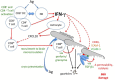
References
-
- Adam R., Russing D., Adams O., Ailyati A., Sik Kim K., Schroten H., et al. (2005). Role of human brain microvascular endothelial cells during central nervous system infection. Significance of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in antimicrobial defence and immunoregulation. Thromb. Haemost. 94, 341–346 10.1267/THRO05020341 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amani V., Vigario A. M., Belnoue E., Marussig M., Fonseca L., Mazier D., et al. (2000). Involvement of IFN-gamma receptor-mediated signaling in pathology and anti-malarial immunity induced by Plasmodium berghei infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 30, 1646–1655 10.1002/1521-4141(200006)30:6<1646::AID-IMMU1646>3.0.CO;2-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

