The surging role of Chromogranin A in cardiovascular homeostasis
- PMID: 25177680
- PMCID: PMC4132265
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2014.00064
The surging role of Chromogranin A in cardiovascular homeostasis
Abstract
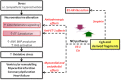
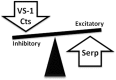
Together with Chromogranin B and Secretogranins, Chromogranin A (CGA) is stored in secretory (chromaffin) granules of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and released with noradrenalin and adrenalin. Co-stored within the granule together with neuropeptideY, cardiac natriuretic peptide hormones, several prohormones and their proteolytic enzymes, CGA is a multifunctional protein and a major marker of the sympatho-adrenal neuroendocrine activity. Due to its partial processing to several biologically active peptides, CGA appears an important pro-hormone implicated in relevant modulatory actions on endocrine, cardiovascular, metabolic, and immune systems through both direct and indirect sympatho-adrenergic interactions. As a part of this scenario, we here illustrate the emerging role exerted by the full-length CGA and its three derived fragments, i.e., Vasostatin 1, catestatin and serpinin, in the control of circulatory homeostasis with particular emphasis on their cardio-vascular actions under both physiological and physio-pathological conditions. The Vasostatin 1- and catestatin-induced cardiodepressive influences are achieved through anti-beta-adrenergic-NO-cGMP signaling, while serpinin acts like beta1-adrenergic agonist through AD-cAMP-independent NO signaling. On the whole, these actions contribute to widen our knowledge regarding the sympatho-chromaffin control of the cardiovascular system and its highly integrated "whip-brake" networks.
Keywords: Catestatin; Chromogranin A; Serpinin; Vasostatin 1; adreno-sympathetic control; cardioprotection; endothelial signaling; vasoactive peptides.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The interplay between chromogranin A-derived peptides and cardiac natriuretic peptides in cardioprotection against catecholamine-evoked stress.Regul Pept. 2010 Nov 30;165(1):86-94. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2010.05.005. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Regul Pept. 2010. PMID: 20594992 Review.
-
The novel chromogranin A-derived serpinin and pyroglutaminated serpinin peptides are positive cardiac β-adrenergic-like inotropes.FASEB J. 2012 Jul;26(7):2888-98. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-201111. Epub 2012 Mar 29. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22459152 Free PMC article.
-
Chromogranin A and its fragments in cardiovascular, immunometabolic, and cancer regulation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Nov;1455(1):34-58. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14249. Epub 2019 Oct 6. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 31588572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromogranin-A: a multifaceted cardiovascular role in health and disease.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(24):4042-50. doi: 10.2174/092986712802430009. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22834795 Review.
-
The chromogranin A-derived peptides vasostatin-I and catestatin as regulatory peptides for cardiovascular functions.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Jan 1;85(1):9-16. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp266. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 19640932 Review.
Cited by
-
A complex role of chromogranin A and its peptides in inflammation, autoimmunity, and infections.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1567874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567874. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40370467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered chromogranin A circulating levels in Meniere's disease.Dis Markers. 2015;2015:643420. doi: 10.1155/2015/643420. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Dis Markers. 2015. PMID: 25983374 Free PMC article.
-
Secretogranin III: a diabetic retinopathy-selective angiogenic factor.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Feb;75(4):635-647. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2635-5. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 28856381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of novel loci affecting circulating chromogranins and related peptides.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Jan 1;26(1):233-242. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw380. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28011710 Free PMC article.
-
Chromogranin B Protects Human Umbilical Endothelial Cells against Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 25;25(19):10296. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910296. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelone T., Quintieri A. M., Brar B. K., Limchaiyawat P. T., Tota B., Mahata S. K., et al. (2008). The antihypertensive Chromogranin A peptide catestatin acts as a novel endocrine/ paracrine modulator of cardiac inotropism and lusitropism. Endocrinology 10, 4780–4793 10.1210/en.2008-0318 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angelone T., Quintieri A. M., Pasqua T., Gentile S., Tota B., Mahata S. K., et al. (2012b). Phosphodiesterase type-2 and NO-dependent S-nitrosylation mediate the cardioinhibition of the antihypertensive catestatin. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 302, H431–H442 10.1152/ajpheart.00491.2011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

