A review of the pharmacological properties of insulin degludec and their clinical relevance
- PMID: 25179915
- PMCID: PMC4156782
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-014-0165-y
A review of the pharmacological properties of insulin degludec and their clinical relevance
Abstract
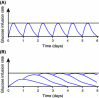
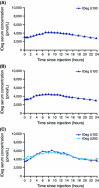
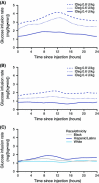
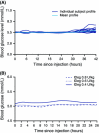
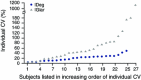
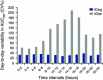
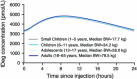
Insulin degludec (IDeg) is a new-generation basal insulin with an ultra-long duration of action. To date, a large number of studies have been conducted to investigate the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of IDeg. Standardised methods for collection and analysis of blood samples (for pharmacokinetic endpoints) and euglycaemic clamp procedures (for pharmacodynamic endpoints) were applied across studies to enable cross-study evaluation of important pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters. Data show that IDeg has a half-life of >25 h [compared with ~12 h for insulin glargine (IGlar)] and reaches steady state within 3 days of administration in all patient populations investigated. The pharmacokinetic profile of IDeg demonstrates an even distribution of exposure across one dosing interval. The pharmacodynamic profile of IDeg is flat and stable, demonstrated by an even distribution of glucose-lowering effect across all four 6-h intervals in a 24-h period (one dosing day). These properties were consistently demonstrated across different type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus patient populations, including those from different ethnic origins (both males and females with type 2 diabetes), the elderly, and patients with hepatic or renal impairment. IDeg has an ultra-long duration of action exceeding 42 h and demonstrates four times lower day-to-day within-subject variability in glucose-lowering effect than IGlar. This review discusses the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data accumulated thus far, and the relevance of these results from a clinical perspective.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of insulin degludec and insulin glargine.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015;11(8):1193-201. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2015.1058779. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26086190 Clinical Trial.
-
Ultra-long pharmacokinetic properties of insulin degludec are comparable in elderly subjects and younger adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Drugs Aging. 2014 Jan;31(1):47-53. doi: 10.1007/s40266-013-0138-0. Drugs Aging. 2014. PMID: 24263619 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic responses of insulin degludec in African American, white, and Hispanic/Latino patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Clin Ther. 2014 Apr 1;36(4):507-15. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.12.014. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Clin Ther. 2014. PMID: 24508419 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical relevance of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of insulin degludec (100, 200 U/mL) and insulin glargine (100, 300 U/mL) - a review of evidence and clinical interpretation.Diabetes Metab. 2019 Sep;45(4):330-340. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2018.11.004. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Diabetes Metab. 2019. PMID: 30496834 Review.
-
Clinical use of insulin degludec.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015 Jul;109(1):19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015. PMID: 25963320 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of insulin glargine 300 units/mL vs insulin degludec in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 19;14:1285147. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1285147. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38313835 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Insulin Degludec in Thai Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Evidence From a Specialized Diabetes Center.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021 Sep;129(9):666-673. doi: 10.1055/a-0899-5118. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 31597169 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin degludec U100 is associated with lower risk for severe and symptomatic hypoglycemia as compared with insulin glargine U100 in subjects with type 1 diabetes.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Feb;6(3):63. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.12.28. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29610753 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Insulin degludec is associated with less frequent and milder hypoglycemia in insulin-deficient patients with type 1 diabetes compared with insulin glargine or detemir.Diabetol Int. 2017 Jan 18;8(2):228-236. doi: 10.1007/s13340-017-0303-5. eCollection 2017 Jun. Diabetol Int. 2017. PMID: 30603326 Free PMC article.
-
Time-action profiles of insulin degludec in healthy dogs and its effects on glycemic control in diabetic dogs.J Vet Med Sci. 2018 Nov 23;80(11):1720-1723. doi: 10.1292/jvms.17-0714. Epub 2018 Oct 11. J Vet Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30305465 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

