Remote effects of lower limb ischemia-reperfusion: impaired lung, unchanged liver, and stimulated kidney oxidative capacities
- PMID: 25180180
- PMCID: PMC4142554
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/392390
Remote effects of lower limb ischemia-reperfusion: impaired lung, unchanged liver, and stimulated kidney oxidative capacities
Abstract
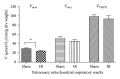
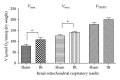
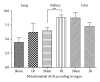
Remote organ impairments are frequent and increase patient morbidity and mortality after lower limb ischemia-reperfusion (IR). We challenged the hypothesis that lower limb IR might also impair lung, renal, and liver mitochondrial respiration. Two-hour tourniquet-induced ischemia was performed on both hindlimbs, followed by a two-hour reperfusion period in C57BL6 mice. Lungs, liver and kidneys maximal mitochondrial respiration (V(max)), complexes II, III, and IV activity (V(succ)), and complex IV activity (V(TMPD)) were analyzed on isolated mitochondria. Lower limb IR decreased significantly lung V(max) (29.4 ± 3.3 versus 24 ± 3.7 μmol O2/min/g dry weight, resp.; P = 0.042) and tended to reduce V(succ) and V(TMPD). IR did not modify liver but increased kidneys mitochondrial respiration (79.5 ± 19.9 versus 108.6 ± 21.4, P = 0.035, and 126 ± 13.4 versus 142.4 ± 10.4 μmol O2/min/g dry weight for V(max) and V(succ), resp.). Kidneys mitochondrial coupling was increased after IR (6.5 ± 1.3 versus 8.8 ± 1.1, P = 0.008). There were no histological changes in liver and kidneys. Thus, lung mitochondrial dysfunction appears as a new early marker of hindlimb IR injuries in mice. Further studies will be useful to determine whether enhanced kidneys mitochondrial function allows postponing kidney impairment in lower limb IR setting.
Figures


References
-
- Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Bell K, et al. Inter-society consensus for the management of peripheral arterial disease (TASC II) European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 2007;33(1, supplement):S1–S75. - PubMed
-
- Lejay A, Meyer A, Schlagowski AI, et al. Mitochondria: mitochondrial participation in ischemia-reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 2014;50:101–105. - PubMed
-
- Kraiss LW, Conte MS, Geary RL, Kibbe M, Ozaki CK. Setting high-impact clinical research priorities for the Society for Vascular Surgery. Journal of Vascular Surgery. 2013;57(2):493–500. - PubMed
-
- Miller CC, III, Villa MA, Sutton J, et al. Serum myoglobin and renal morbidity and mortality following thoracic and thoraco-abdominal aortic repair: does rhabdomyolysis play a role? European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 2009;37(4):388–394. - PubMed
-
- Ali ZA, Callaghan CJ, Lim E, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning reduces myocardial and renal injury after elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a randomized controlled trial. Circulation. 2007;116(11):I98–I105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

