Mapping human brain networks with cortico-cortical evoked potentials
- PMID: 25180306
- PMCID: PMC4150303
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0528
Mapping human brain networks with cortico-cortical evoked potentials
Abstract
The cerebral cortex forms a sheet of neurons organized into a network of interconnected modules that is highly expanded in humans and presumably enables our most refined sensory and cognitive abilities. The links of this network form a fundamental aspect of its organization, and a great deal of research is focusing on understanding how information flows within and between different regions. However, an often-overlooked element of this connectivity regards a causal, hierarchical structure of regions, whereby certain nodes of the cortical network may exert greater influence over the others. While this is difficult to ascertain non-invasively, patients undergoing invasive electrode monitoring for epilepsy provide a unique window into this aspect of cortical organization. In this review, we highlight the potential for cortico-cortical evoked potential (CCEP) mapping to directly measure neuronal propagation across large-scale brain networks with spatio-temporal resolution that is superior to traditional neuroimaging methods. We first introduce effective connectivity and discuss the mechanisms underlying CCEP generation. Next, we highlight how CCEP mapping has begun to provide insight into the neural basis of non-invasive imaging signals. Finally, we present a novel approach to perturbing and measuring brain network function during cognitive processing. The direct measurement of CCEPs in response to electrical stimulation represents a potentially powerful clinical and basic science tool for probing the large-scale networks of the human cerebral cortex.
Keywords: cortico-cortical evoked potential; effective connectivity; electrocorticography; graph theory; stimulation.
© 2014 The Author(s) Published by the Royal Society. All rights reserved.
Figures
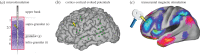
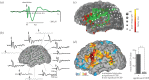

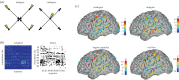
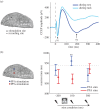
References
-
- Sporns O. 2012. Discovering the human connectome. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
