Plasma PCSK9 levels are elevated with acute myocardial infarction in two independent retrospective angiographic studies
- PMID: 25180781
- PMCID: PMC4152257
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106294
Plasma PCSK9 levels are elevated with acute myocardial infarction in two independent retrospective angiographic studies
Abstract
Objective: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is a circulating protein that promotes degradation of the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor. Mutations that block PCSK9 secretion reduce LDL-cholesterol and the incidence of myocardial infarction (MI). However, it remains unclear whether elevated plasma PCSK9 associates with coronary atherosclerosis (CAD) or more directly with rupture of the plaque causing MI.
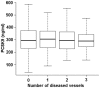
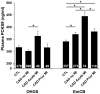
Methods and results: Plasma PCSK9 was measured by ELISA in 645 angiographically defined controls (<30% coronary stenosis) and 3,273 cases of CAD (>50% stenosis in a major coronary artery) from the Ottawa Heart Genomics Study. Because lipid lowering medications elevated plasma PCSK9, confounding association with disease, only individuals not taking a lipid lowering medication were considered (279 controls and 492 with CAD). Replication was sought in 357 controls and 465 with CAD from the Emory Cardiology Biobank study. PCSK9 levels were not associated with CAD in Ottawa, but were elevated with CAD in Emory. Plasma PCSK9 levels were elevated in 45 cases with acute MI (363.5±140.0 ng/ml) compared to 398 CAD cases without MI (302.0±91.3 ng/ml, p = 0.004) in Ottawa. This finding was replicated in the Emory study in 74 cases of acute MI (445.0±171.7 ng/ml) compared to 273 CAD cases without MI (369.9±139.1 ng/ml, p = 3.7×10(-4)). Since PCSK9 levels were similar in CAD patients with or without a prior (non-acute) MI, our finding suggests that plasma PCSK9 is elevated either immediately prior to or at the time of MI.
Conclusion: Plasma PCSK9 levels are increased with acute MI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cohen JC, Boerwinkle E, Mosley TH Jr, Hobbs HH (2006) Sequence variations in PCSK9, low LDL, and protection against coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med 354: 1264–1272. - PubMed
-
- Kathiresan S (2008) A PCSK9 missense variant associated with a reduced risk of early-onset myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 358: 2299–2300. - PubMed
-
- Benn M, Nordestgaard BG, Grande P, Schnohr P, Tybjaerg-Hansen A (2010) PCSK9 R46L, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, and risk of ischemic heart disease: 3 independent studies and meta-analyses. J Am Coll Cardiol 55: 2833–2842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

