Analysis of physical parameters and determination of inflection point for Flattening Filter Free beams in medical linear accelerator
- PMID: 25184057
- PMCID: PMC4150098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2014.01.004
Analysis of physical parameters and determination of inflection point for Flattening Filter Free beams in medical linear accelerator
Abstract
Background: Medical Linear accelerators manufactured without flattening filters are increasing popular in recent days. The removal of flattening filter results in increased dose rate, reduced mean energy, reduction in head leakage and lateral scattering, which have shown advantageous when used for special treatment procedures.
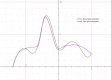
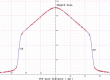
Aim: This study aims to analyze physical parameters of FFF beams and to determine the inflection point for standardizing the beam flatness and penumbra.
Materials and methods: The beam profiles and depth dose patterns were measured using Radiation Field Analyzer (RFA) with 0.13 cc cylindrical ion chamber. The beam energy characteristics, head scatter factor (Sc) were obtained for 6FFF and 10FFF beams and compared with 6 MV and 10 MV photons, respectively. The symmetry and stability of unflattened regions were also analyzed. In addition, the study proposes a simple physical concept for obtaining inflection point for FFF beams and results were compared using the Akima spline interpolation method. The inflection point was used to determine the field size and penumbra of FFF beams.
Results: The Sc varied from 0.922 to 1.044 for 6FFF and from 0.913 to 1.044 for 10FFF with field sizes from 3 cm × 3 cm to 40 cm × 40 cm which is much less than FF beams. The obtained value of field size and penumbra for both simple physical concept and Akima spline interpolation methods is within the ±1.0 mm for the field size and ±2 mm penumbra. The results indicate that FFF beams reduce Sc compared with FF beams due to the absence of a flattening filter.
Conclusion: The proposed simple method to find field size and penumbra using inflection point can be accepted as it is closely approximated to mathematical results. Stability of these parameters was ascertained by repeated measurements and the study indicates good stability for FFF beam similar to that of FF beams.
Keywords: Beam flatness; Flattening Filter Free photons (FFF); Inflection points.
Figures





References
-
- Khan F.M. 4th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Phelidelpeya: 2010. The physics of radiation therapy; pp. 39–40.
-
- Mayles P. Taylor & Francis; Boca Raton, FL: 2007. Handbook of radiotherapy physics. Theory and practice; pp. 215–216.
-
- Ponisch F., Titt U., Oleg N., Vassiliev S.K., Mohan R. Properties of unflattened photon beams shaped by a multi-leaf collimator. Med Phys. 2006;33:1738–1746. - PubMed
-
- Georg D., Knoos T., McClean B. Current status and future perspective of flattening filter free photon beams. Med Phys. 2011;38(3):1280–1293. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

