Antiproliferative activity of hamigerone and radicinol isolated from Bipolaris papendorfii
- PMID: 25184147
- PMCID: PMC4145737
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/890904
Antiproliferative activity of hamigerone and radicinol isolated from Bipolaris papendorfii
Abstract
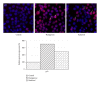
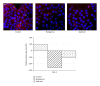
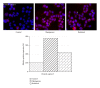
Secondary metabolites from fungi organisms have extensive past and present use in the treatment of many diseases and serve as compounds of interest both in their natural form and as templates for synthetic modification. Through high throughput screening (HTS) and bioassay-guided isolation, we isolated two bioactive compounds hamigerone (1) and radicinol (2). These compounds were isolated from fungus Bipolaris papendorfii, isolated from the rice fields of Dera, Himachal Pradesh, India. The structures of the compounds were established on the basis of spectroscopic data, namely, NMR ((1)H, (13)C, mass, and UV). Both compounds were found to be antiproliferative against different cancer cells. Furthermore we have also noted that both compounds showed increase in apoptosis by favorably modulating both tumor suppressor protein (p53) and antiapoptic protein (BCL-2), and in turn increase caspase-3 expression in cancer cells. This is the first report of these compounds from fungus Bipolaris papendorfii and their anticancer activity.
Figures


References
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. Journal of Natural Products. 2007;70(3):461–477. - PubMed
-
- Frisvad JC, Thrane U, Filtenborg O. Role and use of metabolites in fungal taxonomy. In: Frisvad JC, Bridge PD, Arora DK, editors. Chemical Fungal Taxonomy. New York, NY, USA: Marcel Dekker; 1998. pp. 289–319.
-
- Wang J, Wiltshire T, Wang Y, et al. ATM-dependent CHK2 activation induced by anticancer agent, irofulven. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279(38):39584–39592. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

