Monitoring and evaluation of alcoholic fermentation processes using a chemocapacitor sensor array
- PMID: 25184490
- PMCID: PMC4208173
- DOI: 10.3390/s140916258
Monitoring and evaluation of alcoholic fermentation processes using a chemocapacitor sensor array
Abstract
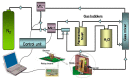
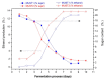
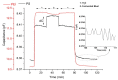
The alcoholic fermentation of Savatiano must variety was initiated under laboratory conditions and monitored daily with a gas sensor array without any pre-treatment steps. The sensor array consisted of eight interdigitated chemocapacitors (IDCs) coated with specific polymers. Two batches of fermented must were tested and also subjected daily to standard chemical analysis. The chemical composition of the two fermenting musts differed from day one of laboratory monitoring (due to different storage conditions of the musts) and due to a deliberate increase of the acetic acid content of one of the musts, during the course of the process, in an effort to spoil the fermenting medium. Sensor array responses to the headspace of the fermenting medium were compared with those obtained either for pure or contaminated samples with controlled concentrations of standard ethanol solutions of impurities. Results of data processing with Principal Component Analysis (PCA), demonstrate that this sensing system could discriminate between a normal and a potential spoiled grape must fermentation process, so this gas sensing system could be potentially applied during wine production as an auxiliary qualitative control instrument.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Volatile compounds formation in alcoholic fermentation from grapes collected at 2 maturation stages: influence of nitrogen compounds and grape variety.J Food Sci. 2012 Jan;77(1):C71-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02441.x. Epub 2011 Nov 1. J Food Sci. 2012. PMID: 22260103
-
Influence of new generation fungicides on Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth, grape must fermentation and aroma biosynthesis.Food Chem. 2014 Mar 1;146:234-41. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.058. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24176337
-
Redox effect on volatile compound formation in wine during fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Food Chem. 2012 Sep 15;134(2):933-9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.209. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 23107710
-
Grape contribution to wine aroma: production of hexyl acetate, octyl acetate, and benzyl acetate during yeast fermentation is dependent upon precursors in the must.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Mar 14;60(10):2638-46. doi: 10.1021/jf2042517. Epub 2012 Feb 29. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22332880
-
The impact of acetate metabolism on yeast fermentative performance and wine quality: reduction of volatile acidity of grape musts and wines.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Jan;89(2):271-80. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2898-3. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20931186 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in electronic nose techniques for monitoring of fermentation process.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Dec;31(12):1845-52. doi: 10.1007/s11274-015-1940-0. Epub 2015 Sep 4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26338367 Review.
-
Proposed SmartBarrel System for Monitoring and Assessment of Wine Fermentation Processes Using IoT Nose and Tongue Devices.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 21;25(13):3877. doi: 10.3390/s25133877. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648136 Free PMC article.
-
Online Monitoring of Sourdough Fermentation Using a Gas Sensor Array with Multivariate Data Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 6;23(18):7681. doi: 10.3390/s23187681. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pinheiro C., Rodrigues C., Schäfer T., Crespo J. Monitoring the aroma production during wine-must fermentation with an electronic nose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002;77:632–640. - PubMed
-
- Ragazzo-Sanchez J.A., Chalier P., Ghommidh C. Coupling gas chromatography and electronic nose for dehydration and desalcoholization of alcoholized beverages. Application to off-flavour detection in wine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005;106:253–257.
-
- Santos J.P., Arroya T., Aleixandre M., Lozano J., Sayago I., García M., Fernandez M.J., Ares L., Gutierrez J., Cabellos J.M., et al. A comparative study of sensor array and GC-MS: Application to Madrid wines characterization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004;102:299–307.
-
- Mamede M.E.O., Pastore G.M. Study of methods for the extraction of volatile compounds from fermented grape must. Food Chem. 2006;96:586–590.
-
- Guadarrama A., Fernandez J.A., Iniguez M., Souto J., de Saja J.A. Discrimination of wine aroma using an array of conducting polymer sensors in conjuction with solid- phase micro-extraction (SPME) technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001;77:401–408.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

