Insight into glycoside hydrolases for debranched xylan degradation from extremely thermophilic bacterium Caldicellulosiruptor lactoaceticus
- PMID: 25184498
- PMCID: PMC4153629
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106482
Insight into glycoside hydrolases for debranched xylan degradation from extremely thermophilic bacterium Caldicellulosiruptor lactoaceticus
Abstract
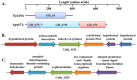
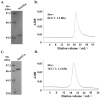
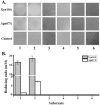
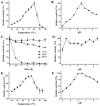
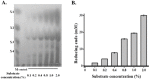
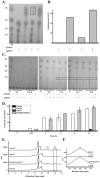
Caldicellulosiruptor lactoaceticus 6A, an anaerobic and extremely thermophilic bacterium, uses natural xylan as carbon source. The encoded genes of C. lactoaceticus 6A for glycoside hydrolase (GH) provide a platform for xylan degradation. The GH family 10 xylanase (Xyn10A) and GH67 α-glucuronidase (Agu67A) from C. lactoaceticus 6A were heterologously expressed, purified and characterized. Both Xyn10A and Agu67A are predicted as intracellular enzymes as no signal peptides identified. Xyn10A and Agu67A had molecular weight of 47.0 kDa and 80.0 kDa respectively as determined by SDS-PAGE, while both appeared as homodimer when analyzed by gel filtration. Xyn10A displayed the highest activity at 80 °C and pH 6.5, as 75 °C and pH 6.5 for Agu67A. Xyn10A had good stability at 75 °C, 80 °C, and pH 4.5-8.5, respectively, and was sensitive to various metal ions and reagents. Xyn10A possessed hydrolytic activity towards xylo-oligosaccharides (XOs) and beechwood xylan. At optimum conditions, the specific activity of Xyn10A was 44.6 IU/mg with beechwood xylan as substrate, and liberated branched XOs, xylobiose, and xylose. Agu67A was active on branched XOs with methyl-glucuronic acids (MeGlcA) sub-chains, and primarily generated XOs equivalents and MeGlcA. The specific activity of Agu67A was 1.3 IU/mg with aldobiouronic acid as substrate. The synergistic action of Xyn10A and Agu67A was observed with MeGlcA branched XOs and xylan as substrates, both backbone and branched chain of substrates were degraded, and liberated xylose, xylobiose, and MeGlcA. The synergism of Xyn10A and Agu67A provided not only a thermophilic method for natural xylan degradation, but also insight into the mechanisms for xylan utilization of C. lactoaceticus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A mini review of xylanolytic enzymes with regards to their synergistic interactions during hetero-xylan degradation.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Nov 14;35(12):187. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2765-z. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31728656 Review.
-
Distinct roles of carbohydrate esterase family CE16 acetyl esterases and polymer-acting acetyl xylan esterases in xylan deacetylation.J Biotechnol. 2013 Dec;168(4):684-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Oct 18. J Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24140638
-
Expression and characterization of a novel halophilic GH10 β-1,4-xylanase from Trichoderma asperellum ND-1 and its synergism with a commercial α-L-arabinofuranosidase on arabinoxylan degradation.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;282(Pt 2):136885. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136885. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39454924
-
GH30-7 Endoxylanase C from the Filamentous Fungus Talaromyces cellulolyticus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Oct 30;85(22):e01442-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01442-19. Print 2019 Nov 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31492671 Free PMC article.
-
Xylanases of glycoside hydrolase family 30 - An overview.Biotechnol Adv. 2021 Mar-Apr;47:107704. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107704. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Biotechnol Adv. 2021. PMID: 33548454 Review.
Cited by
-
The biology and biotechnology of the genus Caldicellulosiruptor: recent developments in 'Caldi World'.Extremophiles. 2020 Jan;24(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s00792-019-01116-5. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Extremophiles. 2020. PMID: 31359136 Review.
-
Characterization of hemicellulase and cellulase from the extremely thermophilic bacterium Caldicellulosiruptor owensensis and their potential application for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass without pretreatment.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015 Aug 28;8:131. doi: 10.1186/s13068-015-0313-0. eCollection 2015. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015. PMID: 26322125 Free PMC article.
-
A mini review of xylanolytic enzymes with regards to their synergistic interactions during hetero-xylan degradation.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Nov 14;35(12):187. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2765-z. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31728656 Review.
-
The extracellular endo-β-1,4-xylanase with multidomain from the extreme thermophile Caldicellulosiruptor lactoaceticus is specific for insoluble xylan degradation.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Jun 8;12:143. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1480-1. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31198440 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling Synergism between Various GH Family Xylanases and Debranching Enzymes during Hetero-Xylan Degradation.Molecules. 2021 Nov 9;26(22):6770. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226770. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34833862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tony C, Charles G, Georges F (2005) Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29: 3–23. - PubMed
-
- Puls J, Schmidt O, Granzow C (1987) α-Glucuronidase in two microbial xylanolytic systems. Enzyme Microb Technol 9: 83–88.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

