AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer
- PMID: 25184630
- PMCID: PMC4201502
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1315815
AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: The androgen-receptor isoform encoded by splice variant 7 lacks the ligand-binding domain, which is the target of enzalutamide and abiraterone, but remains constitutively active as a transcription factor. We hypothesized that detection of androgen-receptor splice variant 7 messenger RNA (AR-V7) in circulating tumor cells from men with advanced prostate cancer would be associated with resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone.
Methods: We used a quantitative reverse-transcriptase-polymerase-chain-reaction assay to evaluate AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells from prospectively enrolled patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer who were initiating treatment with either enzalutamide or abiraterone. We examined associations between AR-V7 status (positive vs. negative) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response rates (the primary end point), freedom from PSA progression (PSA progression-free survival), clinical or radiographic progression-free survival, and overall survival.
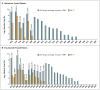
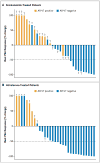
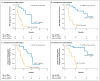
Results: A total of 31 enzalutamide-treated patients and 31 abiraterone-treated patients were enrolled, of whom 39% and 19%, respectively, had detectable AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells. Among men receiving enzalutamide, AR-V7-positive patients had lower PSA response rates than AR-V7-negative patients (0% vs. 53%, P=0.004) and shorter PSA progression-free survival (median, 1.4 months vs. 6.0 months; P<0.001), clinical or radiographic progression-free survival (median, 2.1 months vs. 6.1 months; P<0.001), and overall survival (median, 5.5 months vs. not reached; P=0.002). Similarly, among men receiving abiraterone, AR-V7-positive patients had lower PSA response rates than AR-V7-negative patients (0% vs. 68%, P=0.004) and shorter PSA progression-free survival (median, 1.3 months vs. not reached; P<0.001), clinical or radiographic progression-free survival (median, 2.3 months vs. not reached; P<0.001), and overall survival (median, 10.6 months vs. not reached, P=0.006). The association between AR-V7 detection and therapeutic resistance was maintained after adjustment for expression of full-length androgen receptor messenger RNA.
Conclusions: Detection of AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells from patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer may be associated with resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone. These findings require large-scale prospective validation. (Funded by the Prostate Cancer Foundation and others.).
Figures
Comment in
-
Targeting the androgen receptor in prostate cancer--a resilient foe.N Engl J Med. 2014 Sep 11;371(11):1067-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1409306. Epub 2014 Sep 3. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25184629 No abstract available.
-
Prostate cancer: predicting resistance-AR-V7 is a potential biomarker.Nat Rev Urol. 2014 Nov;11(11):606. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2014.272. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Nat Rev Urol. 2014. PMID: 25266571 No abstract available.
-
Resistance to androgen-pathway drugs in prostate cancer.N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 4;371(23):2234. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1412594. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25470700 No abstract available.
-
Resistance to androgen-pathway drugs in prostate cancer.N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 4;371(23):2233. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1412594. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25470701 No abstract available.
-
Resistance to androgen-pathway drugs in prostate cancer.N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 4;371(23):2233-4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1412594. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25470702 No abstract available.
-
Resistance to androgen-pathway drugs in prostate cancer.N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 4;371(23):2234. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1412594. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25470703 No abstract available.
-
Androgen receptor variant-7: an important predictive biomarker in castrate resistant prostate cancer.Asian J Androl. 2015 May-Jun;17(3):439-40. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.145069. Asian J Androl. 2015. PMID: 25532583 Free PMC article.
-
Enzalutamide for treatment of CRPC: rationale for sequencing and potential clinical biomarker for resistance.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(2):201-3. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.987575. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25569176 Free PMC article.
-
Re: AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer.J Urol. 2015 Feb;193(2):538. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.11.066. Epub 2014 Nov 15. J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25617272 No abstract available.
-
Re: AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer.Eur Urol. 2015 Feb;67(2):349-50. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.11.020. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25760252 No abstract available.
-
Re: AR-V7 and Resistance to Enzalutamide and Abiraterone in Prostate Cancer.Eur Urol. 2015 Jul;68(1):162-3. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.03.054. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 26088731 No abstract available.
-
Commentary on "AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer." Antonarakis ES, Lu C, Wang H, Luber B, Nakazawa M, Roeser JC, Chen Y, Mohammad TA, Chen Y, Fedor HL, Lotan TL, Zheng Q, De Marzo AM, Isaacs JT, Isaacs WB, Nadal R, Paller CJ, Denmeade SR, Carducci MA, Eisenberger MA, Luo J, Division of Urologic Oncology, Department of Urology, University of Michigan, MI. N Engl J Med 2014; 371(11):1028-38.Urol Oncol. 2016 Nov;34(11):520. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.12.011. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26964769 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
