High-frequency ultrasound associated with dermoscopy in pre-operative evaluation of basal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25184930
- PMCID: PMC4155969
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20143176
High-frequency ultrasound associated with dermoscopy in pre-operative evaluation of basal cell carcinoma
Abstract
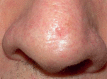
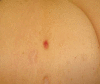
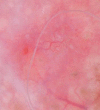
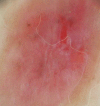
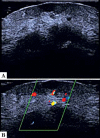
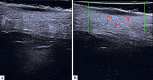
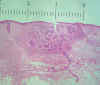
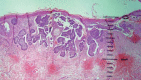
The recent development of high-frequency ultrasound, associated with the improved sensitivity in color Doppler, enabled the identification of various skin structures and layers. In basal cell carcinoma, the 22 MHz frequency ultrasound permits the delimitation of tumor margins, while color Doppler, determines its vascularization. We present two cases in which the association of both exams allowed an in vivo analysis of the tumor's morphology, size, thickness and vascularization, thus contributing to a better pre-operative evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Wortsman X, Wortsman J. Clinical usefulness of variable-frequency ultrasound in localized lesions of the skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:247–256. - PubMed
-
- Kleinerman R, Whang TB, Bard RL, Marmur ES. Ultrasound in dermatology: principles and applications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:478–487. - PubMed
-
- Wortsman X. Common Applications of Dermatologic Sonography. J Ultrasound Med. 2012;31:97–111. - PubMed
-
- Crisan M, Crisan D, Sannino G, Lupsor M, Badea R, Amzica F. Ultrasonographic staging of cutaneous malignant tumors: an ultrasonographic depth index. Arch Dermatol Res. 2013;305:305–313. - PubMed
-
- Altamura D, Menzies SW, Argenziano G, Zalaudek I, Soyer HP, Sera F, et al. Dermatoscopy of basal cell carcinoma: Morphologic variability of global and local features and accuracy of diagnosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:67–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
