Malaria in Brazil: what happens outside the Amazonian endemic region
- PMID: 25185003
- PMCID: PMC4156455
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-0276140228
Malaria in Brazil: what happens outside the Amazonian endemic region
Erratum in
-
ERRATUM: "Malaria in Brazil: what happens outside the Amazonian endemic region".Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2018 Aug 27;113(9):e140228ER. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760140228ER. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2018. PMID: 30156599 Free PMC article.
Abstract
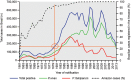
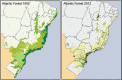
Brazil, a country of continental proportions, presents three profiles of malaria transmission. The first and most important numerically, occurs inside the Amazon. The Amazon accounts for approximately 60% of the nation's territory and approximately 13% of the Brazilian population. This region hosts 99.5% of the nation's malaria cases, which are predominantly caused by Plasmodium vivax (i.e., 82% of cases in 2013). The second involves imported malaria, which corresponds to malaria cases acquired outside the region where the individuals live or the diagnosis was made. These cases are imported from endemic regions of Brazil (i.e., the Amazon) or from other countries in South and Central America, Africa and Asia. Imported malaria comprised 89% of the cases found outside the area of active transmission in Brazil in 2013. These cases highlight an important question with respect to both therapeutic and epidemiological issues because patients, especially those with falciparum malaria, arriving in a region where the health professionals may not have experience with the clinical manifestations of malaria and its diagnosis could suffer dramatic consequences associated with a potential delay in treatment. Additionally, because the Anopheles vectors exist in most of the country, even a single case of malaria, if not diagnosed and treated immediately, may result in introduced cases, causing outbreaks and even introducing or reintroducing the disease to a non-endemic, receptive region. Cases introduced outside the Amazon usually occur in areas in which malaria was formerly endemic and are transmitted by competent vectors belonging to the subgenus Nyssorhynchus (i.e., Anopheles darlingi, Anopheles aquasalis and species of the Albitarsis complex). The third type of transmission accounts for only 0.05% of all cases and is caused by autochthonous malaria in the Atlantic Forest, located primarily along the southeastern Atlantic Coast. They are caused by parasites that seem to be (or to be very close to) P. vivax and, in a less extent, by Plasmodium malariae and it is transmitted by the bromeliad mosquito Anopheles (Kerteszia) cruzii. This paper deals mainly with the two profiles of malaria found outside the Amazon: the imported and ensuing introduced cases and the autochthonous cases. We also provide an update regarding the situation in Brazil and the Brazilian endemic Amazon.
Figures



References
-
- Andrade JCR, Anjos CFD, Wanderley DMV, Alves MJC, Campos PC. Foco de malária no estado de São Paulo (Brasil) Rev Saude Publica. 1986;20:323–326. - PubMed
-
- Aragão MB. Sobre a biomassa dos Anopheles do subgênero Kerteszia em seus criadouros. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1968;66:227–237. - PubMed
-
- Azevedo AL. Aspectos da epidemiologia da malária e da biologia de Anopheles (Kerteszia) cruzii Dyar & Knab em vales montanhosos do sistema de Mata Atlântica. Instituto Oswaldo Cruz/Fiocruz; Rio de Janeiro: 1997. 94 MsD Thesis.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

