Characterization of GLPG0492, a selective androgen receptor modulator, in a mouse model of hindlimb immobilization
- PMID: 25185887
- PMCID: PMC4167280
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-291
Characterization of GLPG0492, a selective androgen receptor modulator, in a mouse model of hindlimb immobilization
Abstract
Background: Muscle wasting is a hallmark of many chronic conditions but also of aging and results in a progressive functional decline leading ultimately to disability. Androgens, such as testosterone were proposed as therapy to counteract muscle atrophy. However, this treatment is associated with potential cardiovascular and prostate cancer risks and therefore not acceptable for long-term treatment. Selective Androgen receptor modulators (SARM) are androgen receptor ligands that induce muscle anabolism while having reduced effects in reproductive tissues. Therefore, they represent an alternative to testosterone therapy. Our objective was to demonstrate the activity of SARM molecule (GLPG0492) on a immobilization muscle atrophy mouse model as compared to testosterone propionate (TP) and to identify putative biomarkers in the plasma compartment that might be related to muscle function and potentially translated into the clinical space.
Methods: GLPG0492, a non-steroidal SARM, was evaluated and compared to TP in a mouse model of hindlimb immobilization.
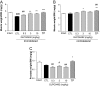
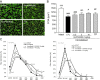
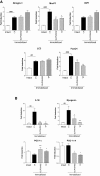
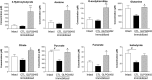
Results: GLPG0492 treatment partially prevents immobilization-induced muscle atrophy with a trend to promote muscle fiber hypertrophy in a dose-dependent manner. Interestingly, GLPG0492 was found as efficacious as TP at reducing muscle loss while sparing reproductive tissues. Furthermore, gene expression studies performed on tibialis samples revealed that both GLPG0492 and TP were slowing down muscle loss by negatively interfering with major signaling pathways controlling muscle mass homeostasis. Finally, metabolomic profiling experiments using 1H-NMR led to the identification of a plasma GLPG0492 signature linked to the modulation of cellular bioenergetic processes.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results unveil the potential of GLPG0492, a non-steroidal SARM, as treatment for, at least, musculo-skeletal atrophy consecutive to coma, paralysis, or limb immobilization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GLPG0492, a novel selective androgen receptor modulator, improves muscle performance in the exercised-mdx mouse model of muscular dystrophy.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Jun;72:9-24. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23523664
-
Comparison of the three SARMs RAD-140, GLPG0492 and GSK-2881078 in two different in vitro bioassays, and in an in silico androgen receptor binding assay.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 May;189:81-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.02.014. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30825507
-
Dietary wild bitter gourd displays selective androgen receptor modulator like activity and improves the muscle decline of orchidectomized mice.Food Funct. 2019 Jan 22;10(1):125-139. doi: 10.1039/c8fo01777h. Food Funct. 2019. PMID: 30600821
-
Selective androgen receptor modulators for the prevention and treatment of muscle wasting associated with cancer.Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2013 Dec;7(4):345-51. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0000000000000015. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2013. PMID: 24189892 Review.
-
Actin associated proteins function as androgen receptor coregulators: an implication of androgen receptor's roles in skeletal muscle.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008 Sep;111(3-5):157-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2008.06.001. Epub 2008 Jun 11. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18590822 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac cachexia: hic et nunc.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2016 Jun;7(3):246-60. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12118. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2016. PMID: 27386168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of body weight loss and sarcopenia by a novel selective androgen receptor modulator in cancer cachexia models.Oncol Lett. 2017 Dec;14(6):8066-8071. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7200. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29344250 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators: Current Knowledge and Clinical Applications.Sex Med Rev. 2019 Jan;7(1):84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Sex Med Rev. 2019. PMID: 30503797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological therapeutics targeting the secondary defects and downstream pathology of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Expert Opin Orphan Drugs. 2016;4(11):1179-1194. doi: 10.1080/21678707.2016.1240613. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Expert Opin Orphan Drugs. 2016. PMID: 28670506 Free PMC article.
-
Androgens Drive Sex Biases in Hypothalamic Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Gene Expression After Adrenalectomy of Mice.Endocrinology. 2019 Jul 1;160(7):1757-1770. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00238. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 31074799 Free PMC article.
References
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2474/15/291/prepub
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

