The genomic substrate for adaptive radiation in African cichlid fish
- PMID: 25186727
- PMCID: PMC4353498
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13726
The genomic substrate for adaptive radiation in African cichlid fish
Abstract
Cichlid fishes are famous for large, diverse and replicated adaptive radiations in the Great Lakes of East Africa. To understand the molecular mechanisms underlying cichlid phenotypic diversity, we sequenced the genomes and transcriptomes of five lineages of African cichlids: the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), an ancestral lineage with low diversity; and four members of the East African lineage: Neolamprologus brichardi/pulcher (older radiation, Lake Tanganyika), Metriaclima zebra (recent radiation, Lake Malawi), Pundamilia nyererei (very recent radiation, Lake Victoria), and Astatotilapia burtoni (riverine species around Lake Tanganyika). We found an excess of gene duplications in the East African lineage compared to tilapia and other teleosts, an abundance of non-coding element divergence, accelerated coding sequence evolution, expression divergence associated with transposable element insertions, and regulation by novel microRNAs. In addition, we analysed sequence data from sixty individuals representing six closely related species from Lake Victoria, and show genome-wide diversifying selection on coding and regulatory variants, some of which were recruited from ancient polymorphisms. We conclude that a number of molecular mechanisms shaped East African cichlid genomes, and that amassing of standing variation during periods of relaxed purifying selection may have been important in facilitating subsequent evolutionary diversification.
Figures
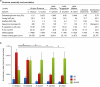


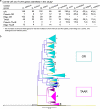
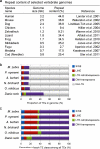
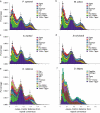

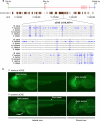
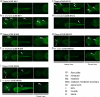



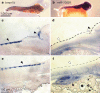

Comment in
-
Evolutionary biology: Radiating genomes.Nature. 2014 Sep 18;513(7518):318-9. doi: 10.1038/nature13742. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25186726 No abstract available.
-
Evolution: a fishy tale of adaptive radiation.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Nov;15(11):704. doi: 10.1038/nrg3835. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25246195 No abstract available.
References
-
- Darwin C. On the Origin of Species. 6th edn John Murray; 1859.
-
- Simpson GG. Tempo and Mode in Evolution. Columbia Univ. Press; 1944.
-
- Kocher TD. Adaptive evolution and explosive speciation: the cichlid fish model. Nature Rev. Genet. 2004;5:288–298. - PubMed
-
- Wagner CE, Harmon LJ, Seehausen O. Ecological opportunity and sexual selection together predict adaptive radiation. Nature. 2012;487:366–369. - PubMed
-
- Meyer A. Morphometrics and allometry in the trophically polymorphic cichlid fish, Cichlasoma citrinellum: alternative adaptations and ontogenic changes in shape. J. Zool. 1990;221:237–260.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- BioProject/PRJNA221867
- BioProject/PRJNA221871
- BioProject/PRJNA222489
- BioProject/PRJNA222490
- BioProject/PRJNA222491
- BioProject/PRJNA59571
- BioProject/PRJNA60363
- BioProject/PRJNA60365
- BioProject/PRJNA60367
- BioProject/PRJNA60369
- BioProject/PRJNA77743
- BioProject/PRJNA77747
- BioProject/PRJNA78185
- BioProject/PRJNA78915
- BioProject/PRJNA83153
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

