Measuring extracellular pH in a lung fibrosis model with acidoCEST MRI
- PMID: 25187227
- PMCID: PMC4832114
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-014-0784-6
Measuring extracellular pH in a lung fibrosis model with acidoCEST MRI
Abstract
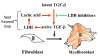
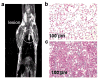
Purpose: A feed-forward loop involving lactic acid production may potentially occur during the formation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. To provide evidence for this feed-forward loop, we used acidoCEST MRI to measure the extracellular pH (pHe), while also measuring percent uptake of the contrast agent, lesion size, and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC).
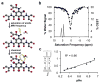
Procedures: We developed a respiration-gated version of acidoCEST MRI to improve the measurement of pHe and percent uptake in lesions. We also used T2-weighted MRI to measure lesion volumes and diffusion-weighted MRI to measure ADC.
Results: The longitudinal changes in average pHe and % uptake of the contrast agent were inversely related to reduction in lung lesion volume. The average ADC did not change during the time frame of the study.
Conclusions: The increase in pHe during the reduction in lesion volume indicates a role for lactic acid in the proposed feed-forward loop of IPF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nathan SD, Shlobin OA, Weir N, et al. Long-term course and prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the new millennium. Chest. 2011;140:221–229. - PubMed
-
- Ley B, Collard HR, King TE., Jr Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:431–440. - PubMed
-
- Sime PJ, Samstrand B, Xing Z, et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of the proteoglycan biglycan induces fibroblastic responses in the lung. Chest. 1997;111:137S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

