High infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages in triple-negative breast cancer is associated with a higher risk of distant metastasis
- PMID: 25187727
- PMCID: PMC4149399
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S61838
High infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages in triple-negative breast cancer is associated with a higher risk of distant metastasis
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is associated with poor prognosis and high probability of distant metastases. Tumor microenvironments play a pivotal role in tumor metastasis. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are one of the main cell components, and they are correlated with increasing metastatic risk. The aim of this study is to analyze the prognostic significance of the infiltration of TAMs in patients with TNBC.
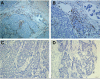
Materials and methods: Immunohistochemical staining for cluster of differentiation (CD)68 (a marker for macrophages) was performed on tissue microarrays of operable breast cancer among 287 patients with TNBC, and the number of infiltrating TAMs was correlated with clinicopathological parameters.
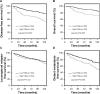
Results: We found that TNBC with a large number of infiltrating TAMs had a significantly higher risk of distant metastasis, as well as lower rates of disease-free survival and overall survival than those with a smaller number of infiltrating TAMs. Multivariate analysis indicated that the number of infiltrating TAMs was a significant independent prognostic factor of disease-free survival (P=0.001) in all patients.
Conclusion: Our results suggested that high infiltrating TAMs are a significantly unfavorable prognostic factor for patients with TNBC, and they could become a potentially useful prognostic marker for TNBC.
Keywords: breast carcinoma; prognosis; triple-negative; tumor-associated macrophages.
Figures
References
-
- Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–752. - PubMed
-
- Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006;295(21):2492–2502. - PubMed
-
- Desmedt C, Haibe-Kains B, Wirapati P, et al. Biological processes associated with breast cancer clinical outcome depend on the molecular subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(16):5158–5165. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

