Astragaloside IV inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-BB-stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via the inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling
- PMID: 25187834
- PMCID: PMC4151649
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1905
Astragaloside IV inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-BB-stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via the inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Astragaloside IV inhibits platelet‑derived growth factor‑BB‑stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via the inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Oct 16;26(6):550. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12250. eCollection 2023 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37928512 Free PMC article.
Abstract
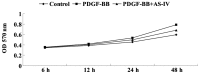
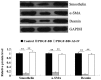
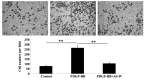
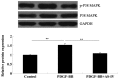
Astragaloside IV (AS-IV), the major active component extracted from Astragalus membranaceus, has been demonstrated to exhibit protective effects on the cardiovascular, immune, digestive and nervous systems; thus, has been widely used in traditional Chinese medicine. Abnormal proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) is closely associated with the initiation and progression of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis and restenosis. However, the effects of AS-IV on VSMCs remain unknown. For the first time, the present study demonstrated that AS-IV markedly suppressed platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB-stimulated cellular proliferation and migration of HDMEC-a human dermal VSMCs (HDVSMCs). Further investigation into the underlying molecular mechanisms demonstrated that the administration of AS-IV attenuated the PDGF-BB-stimulated switch of HDVSMCs into a proliferative phenotype. Furthermore, AS-IV inhibited the PDGF-BB-induced expression of cell cycle-associated proteins, as well as the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)2, but not MMP9. In addition, AS-IV was shown to downregulate the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling induced by PDGF-BB in HDVSMCs. Therefore, the observations of the present study indicate that AS-IV inhibits PDGF-BB-stimulated VSMC proliferation and migration, possibly by inhibiting the activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Thus, AS-IV may be useful for the treatment of vascular diseases.
Keywords: astragaloside IV; migration; platelet-derived growth factor; proliferation; vascular smooth muscle cell.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppressive effect of formononetin on platelet-derived growth factor-BB-stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Sep;12(3):1901-1907. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3514. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27588108 Free PMC article.
-
Ligustrazine attenuates the platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells by interrupting extracellular signal-regulated kinase and P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):705-11. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3383. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25738255
-
Rosuvastatin suppresses platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via the MAPK signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2013 Oct;6(4):899-903. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1265. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Exp Ther Med. 2013. Retraction in: Exp Ther Med. 2023 Nov 13;27(1):11. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12299. PMID: 24137286 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Low-power laser irradiation inhibits PDGF-BB-induced migration and proliferation via apoptotic cell death in vascular smooth muscle cells.Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Dec;32(9):2121-2127. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2338-z. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28983687
-
Inhibitory effects of Brazilin on the vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration induced by PDGF-BB.Am J Chin Med. 2013;41(6):1283-96. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X13500869. Am J Chin Med. 2013. PMID: 24228601
Cited by
-
Astragaloside IV ameliorates necrotizing enterocolitis by attenuating oxidative stress and suppressing inflammation via the vitamin D3-upregulated protein 1/NF-κB signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Oct;12(4):2702-2708. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3629. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27698775 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased S100A9 Expression Promoted Rat Airway Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation by Stimulating ROS Generation and Inhibiting p38 MAPK.Can Respir J. 2016;2016:1462563. doi: 10.1155/2016/1462563. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Can Respir J. 2016. PMID: 28050155 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Protective Function of 5-Methoxytryptophan in Vascular Injury.Sci Rep. 2016 May 5;6:25374. doi: 10.1038/srep25374. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27146795 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressive effect of formononetin on platelet-derived growth factor-BB-stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Sep;12(3):1901-1907. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3514. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27588108 Free PMC article.
-
[Galangin inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced angiogenic activity in human aortic endothelial cells by downregulating lncRNA H19].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Jan 20;44(1):52-59. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.01.07. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38293976 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Ren S, Zhang H, Mu Y, Sun M, Liu P. Pharmacological effects of Astragaloside IV: a literature review. J Tradit Chin Med. 2013;33:413–416. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Hu G, Li S, et al. Pro-angiogenic activity of astragaloside IV in HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5:805–811. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Liu Q, Lu L, Zhao X, Gao X, Wang Y. Astragaloside IV stimulates angiogenesis and increases hypoxia-inducible factor-1α accumulation via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;338:485–491. - PubMed
-
- Choe N, Kwon JS, Kim JR, et al. The microRNA miR-132 targets Lrrfip1 to block vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. Atherosclerosis. 2013;229:348–355. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
