Surgery-related complications and sequelae in management of tuberculosis of spine
- PMID: 25187860
- PMCID: PMC4149986
- DOI: 10.4184/asj.2014.8.4.435
Surgery-related complications and sequelae in management of tuberculosis of spine
Abstract
Study design: Medical record-based survey.
Purpose: To survey the overall incidence of the intra- and postoperative complications and sequelae, and to propose the preventive measures to reduce complications in the spinal tuberculosis surgery.
Overview of literature: There is no study focused on the surgery-related complications and sequelae, with some touching lightly on the clinical problems.
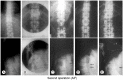
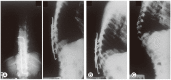
Methods: There were 901 patients in this study, including 92 paraplegics. One hundred eighty-six patients had no visible deformity, while those of 715 patients were visible. Six hundred fifty-nine patients had slight to moderate non-rigid kyphosis, and 56 had severe rigid kyphosis. Sixty-seven out of 92 paraplegics had slight to moderate non-rigid kyphosis, and 25 had severe kyphosis. There were 134 cervical and cervicodorsal lesions, 518 thoracic and thoracolumbar lesions, and 249 lumbar and lumbosacral lesions. Seven hundred sixty-four patients had primarily anterior surgeries, and 137 had posterior surgeries. Instrumentation surgery was combined in 174 patients.
Results: There were intra- and postoperative complications: direct large vessel and neurological injuries (cord, roots, nerves), late thrombophlebitis, various thoracic cavity problems, esophagus and ureter injuries, peritoneum perforation, ileus, wound infections, stabilization failure, increase of deformity and late adjacent joint and bone problems. Thrombophlebitis and sympatheticolysis symptoms and signs in the lower limbs were the most common complications related with anterior lumbar and lumbosacral surgeries. Kyphosis increased in 31.5% of the non-instrumented anterior surgery cases (42% in children and 21% in adults).
Conclusions: The safe, effective and most familiar surgical procedure should be adopted to minimize complications and sequelae. Cosmetic spinal surgery should be withheld if functional improvement could not be expected.
Keywords: Complications; Spine; Surgery; Therapeutics; Tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Chen WJ, Chen CH, Shih CH. Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylitis: 50 patients followed for 2-8 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1995;66:137–142. - PubMed
-
- Cheung KM, Al Ghazi S. Approach-related complications of open versus thoracoscopic anterior exposures of the thoracic spine. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2008;16:343–347. - PubMed
-
- Fountain SS, Hsu LC, Yau AC, Hodgson AR. Progressive kyphosis following solid anterior spine fusion in children with tuberculosis of the spine. A long-term study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57:1104–1107. - PubMed
-
- Faciszewski T, Winter RB, Lonstein JE, Denis F, Johnson L. The surgical and medical perioperative complications of anterior spinal fusion surgery in the thoracic and lumbar spine in adults. A review of 1223 procedures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:1592–1599. - PubMed
-
- Grossfeld S, Winter RB, Lonstein JE, Denis F, Leonard A, Johnson L. Complications of anterior spinal surgery in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997;17:89–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

