Genome-wide association meta-analysis of neuropathologic features of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias
- PMID: 25188341
- PMCID: PMC4154667
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004606
Genome-wide association meta-analysis of neuropathologic features of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias
Erratum in
- PLoS Genet. 2014 Nov;10(11):e1004867
Abstract
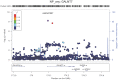
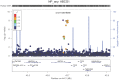
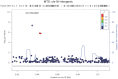
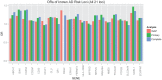
Alzheimer's disease (AD) and related dementias are a major public health challenge and present a therapeutic imperative for which we need additional insight into molecular pathogenesis. We performed a genome-wide association study and analysis of known genetic risk loci for AD dementia using neuropathologic data from 4,914 brain autopsies. Neuropathologic data were used to define clinico-pathologic AD dementia or controls, assess core neuropathologic features of AD (neuritic plaques, NPs; neurofibrillary tangles, NFTs), and evaluate commonly co-morbid neuropathologic changes: cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), Lewy body disease (LBD), hippocampal sclerosis of the elderly (HS), and vascular brain injury (VBI). Genome-wide significance was observed for clinico-pathologic AD dementia, NPs, NFTs, CAA, and LBD with a number of variants in and around the apolipoprotein E gene (APOE). GalNAc transferase 7 (GALNT7), ATP-Binding Cassette, Sub-Family G (WHITE), Member 1 (ABCG1), and an intergenic region on chromosome 9 were associated with NP score; and Potassium Large Conductance Calcium-Activated Channel, Subfamily M, Beta Member 2 (KCNMB2) was strongly associated with HS. Twelve of the 21 non-APOE genetic risk loci for clinically-defined AD dementia were confirmed in our clinico-pathologic sample: CR1, BIN1, CLU, MS4A6A, PICALM, ABCA7, CD33, PTK2B, SORL1, MEF2C, ZCWPW1, and CASS4 with 9 of these 12 loci showing larger odds ratio in the clinico-pathologic sample. Correlation of effect sizes for risk of AD dementia with effect size for NFTs or NPs showed positive correlation, while those for risk of VBI showed a moderate negative correlation. The other co-morbid neuropathologic features showed only nominal association with the known AD loci. Our results discovered new genetic associations with specific neuropathologic features and aligned known genetic risk for AD dementia with specific neuropathologic changes in the largest brain autopsy study of AD and related dementias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Sonnen JA, Larson EB, Crane PK, Haneuse S, Li G, et al. (2007) Pathological correlates of dementia in a longitudinal, population-based sample of aging. Ann Neurol 62: 406–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5R01AG022374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG05144/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH060451/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA137788/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG030514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH60451/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG17917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028377/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036528/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG041232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008671/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG10483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG10133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG035137/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005128/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031581/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016577/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019085/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013616/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029893/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016575/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG05128/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS039764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036502/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UO1 HG004610/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AG035137/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080295/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG03991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026390/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG010491/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG08051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS39764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG012101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG33193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA132378/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2AG036502/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG15819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG026390/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UO1 AG06781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG030653/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R37 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG027944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005144/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG010491/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021547/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041232/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019757/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AG012101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030653/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027944/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG30146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017173/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004610/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016582/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041718/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AG013616/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG019757/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MO1RR00096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026916/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS059873/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG021547/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR02777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

