High density lipoprotein stimulated migration of macrophages depends on the scavenger receptor class B, type I, PDZK1 and Akt1 and is blocked by sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor antagonists
- PMID: 25188469
- PMCID: PMC4154704
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106487
High density lipoprotein stimulated migration of macrophages depends on the scavenger receptor class B, type I, PDZK1 and Akt1 and is blocked by sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor antagonists
Erratum in
-
Correction: High Density Lipoprotein Stimulated Migration of Macrophages Depends on the Scavenger Receptor Class B, Type I, PDZK1 and Akt1 and Is Blocked by Sphingosine 1 Phosphate Receptor Antagonists.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 9;10(1):e0117623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117623. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25574850 Free PMC article.
Abstract
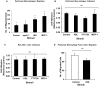
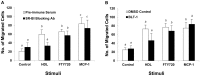
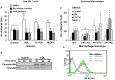
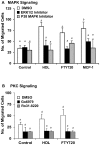
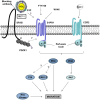
HDL carries biologically active lipids such as sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) and stimulates a variety of cell signaling pathways in diverse cell types, which may contribute to its ability to protect against atherosclerosis. HDL and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonists, FTY720 and SEW2871 triggered macrophage migration. HDL-, but not FTY720-stimulated migration was inhibited by an antibody against the HDL receptor, SR-BI, and an inhibitor of SR-BI mediated lipid transfer. HDL and FTY720-stimulated migration was also inhibited in macrophages lacking either SR-BI or PDZK1, an adaptor protein that binds to SR-BI's C-terminal cytoplasmic tail. Migration in response to HDL and S1P receptor agonists was inhibited by treatment of macrophages with sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor type 1 (S1PR1) antagonists and by pertussis toxin. S1PR1 activates signaling pathways including PI3K-Akt, PKC, p38 MAPK, ERK1/2 and Rho kinases. Using selective inhibitors or macrophages from gene targeted mice, we demonstrated the involvement of each of these pathways in HDL-dependent macrophage migration. These data suggest that HDL stimulates the migration of macrophages in a manner that requires the activities of the HDL receptor SR-BI as well as S1PR1 activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Taylor PR, Martinez-Pomares L, Stacey M, Lin HH, Brown GD, et al. (2005) Macrophage receptors and immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 23: 901–944. - PubMed
-
- Libby P (2002) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420: 868–874. - PubMed
-
- Steinberg D (1997) Low density lipoprotein oxidation and its pathobiological significance. J Biol Chem 272: 20963–20966. - PubMed
-
- Tabas I, Williams KJ, Boren J (2007) Subendothelial lipoprotein retention as the initiating process in atherosclerosis: update and therapeutic implications. Circulation 116: 1832–1844. - PubMed
-
- Nagao T, Qin C, Grosheva I, Maxfield FR, Pierini LM (2007) Elevated cholesterol levels in the plasma membranes of macrophages inhibit migration by disrupting RhoA regulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27: 1596–1602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

