Therapeutic challenges of pancreatic ascites and the role of endoscopic pancreatic stenting
- PMID: 25188928
- PMCID: PMC4154046
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-204774
Therapeutic challenges of pancreatic ascites and the role of endoscopic pancreatic stenting
Abstract
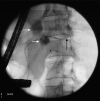
Management of pancreatic ascites poses significant therapeutic challenges. Treatment usually consists of either conservative management or interventional therapy with little consensus between the two options. Conservative therapy is the most common initial treatment option but has high failure rates hence arguing for interventional therapy as a preferred primary treatment option. Endoscopic treatment is particularly appealing due to lower failure rates and mortality than conservative therapy or surgery. We describe a patient with recurrent pancreatic ascites who was successfully managed with endoscopic transpapillary stenting. This report contributes to the limited but growing literature on the management of pancreatic ascites.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Lipsett PA, Cameron JL. Internal pancreatic fistula. Am J Surg 1992;163:216–20 - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Cerezo J, Barbado Cano A, Suarez I, et al. Pancreatic ascites: study of therapeutic options by analysis of case reports and case series between the years 1975 and 2000. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98:568–77 - PubMed
-
- Ohge H, Yokoyama T, Kodama T, et al. Surgical approaches for pancreatic ascites: report of three cases. Surg Today 1999;29:458–61 - PubMed
-
- Parekh D, Segal I. Pancreatic ascites and effusion. Risk factors for failure of conservative therapy and the role of octreotide. Arch Surg 1992;127:707–12 - PubMed
-
- Bracher GA, Manocha AP, DeBanto JR, et al. Endoscopic pancreatic duct stenting to treat pancreatic ascites. Gastrointest Endosc 1999;49:710–15 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
