Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation of RapGEF2 controls neuronal migration in the developing cerebral cortex
- PMID: 25189171
- PMCID: PMC4164783
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5826
Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation of RapGEF2 controls neuronal migration in the developing cerebral cortex
Abstract
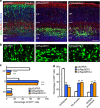
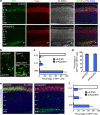
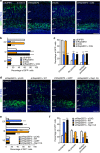
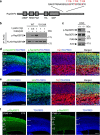
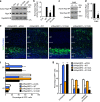
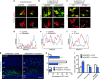
During cerebral cortex development, pyramidal neurons migrate through the intermediate zone and integrate into the cortical plate. These neurons undergo the multipolar-bipolar transition to initiate radial migration. While perturbation of this polarity acquisition leads to cortical malformations, how this process is initiated and regulated is largely unknown. Here we report that the specific upregulation of the Rap1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor, RapGEF2, in migrating neurons corresponds to the timing of this polarity transition. In utero electroporation and live-imaging studies reveal that RapGEF2 acts on the multipolar-bipolar transition during neuronal migration via a Rap1/N-cadherin pathway. Importantly, activation of RapGEF2 is controlled via phosphorylation by a serine/threonine kinase Cdk5, whose activity is largely restricted to the radial migration zone. Thus, the specific expression and Cdk5-dependent phosphorylation of RapGEF2 during multipolar-bipolar transition within the intermediate zone are essential for proper neuronal migration and wiring of the cerebral cortex.
Figures


References
-
- Nadarajah B., Brunstrom J. E., Grutzendler J., Wong R. O. & Pearlman A. L. Two modes of radial migration in early development of the cerebral cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 143–150 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Noctor S. C., Martinez-Cerdeno V., Ivic L. & Kriegstein A. R. Cortical neurons arise in symmetric and asymmetric division zones and migrate through specific phases. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 136–144 (2004). - PubMed
-
- LoTurco J. J. & Bai J. The multipolar stage and disruptions in neuronal migration. Trends Neurosci. 29, 407–413 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Kerjan G. & Gleeson J. G. Genetic mechanisms underlying abnormal neuronal migration in classical lissencephaly. Trends Genet. 23, 623–630 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

