New insights into IL-12-mediated tumor suppression
- PMID: 25190142
- PMCID: PMC4291488
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.134
New insights into IL-12-mediated tumor suppression
Abstract
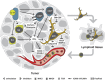
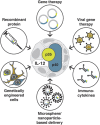
During the past two decades, interleukin-12 (IL-12) has emerged as one of the most potent cytokines in mediating antitumor activity in a variety of preclinical models. Through pleiotropic effects on different immune cells that form the tumor microenvironment, IL-12 establishes a link between innate and adaptive immunity that involves different immune effector cells and cytokines depending on the type of tumor or the affected tissue. The robust antitumor response exerted by IL-12, however, has not yet been successfully translated into the clinics. The majority of clinical trials involving treatment with IL-12 failed to show sustained antitumor responses and were associated to toxic side effects. Here we discuss the therapeutic effects of IL-12 from preclinical to clinical studies, and will highlight promising strategies to take advantage of the antitumor activity of IL-12 while limiting adverse effects.
Figures
References
-
- Trinchieri G, Rengaraju M, D'Andrea A, Valiante NM, Kubin M, Aste M, et al. Producer cells of interleukin 12. Parasitol Today. 1993;9:97. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:135–145. - PubMed
-
- Kuwajima S, Sato T, Ishida K, Tada H, Tezuka H, Ohteki T. Interleukin 15-dependent crosstalk between conventional and plasmacytoid dendritic cells is essential for CpG-induced immune activation. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:740–746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

