Coronary artery manifestations of fibromuscular dysplasia
- PMID: 25190240
- PMCID: PMC4370367
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.07.014
Coronary artery manifestations of fibromuscular dysplasia
Abstract
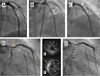
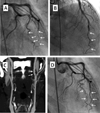
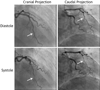
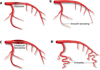
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) involving the coronary arteries is an uncommon but important condition that can present as acute coronary syndrome, left ventricular dysfunction, or potentially sudden cardiac death. Although the classic angiographic "string of beads" that may be observed in renal artery FMD does not occur in coronary arteries, potential manifestations include spontaneous coronary artery dissection, distal tapering or long, smooth narrowing that may represent dissection, intramural hematoma, spasm, or tortuosity. Importantly, FMD must be identified in at least one other noncoronary arterial territory to attribute any coronary findings to FMD. Although there is limited evidence to guide treatment, many lesions heal spontaneously; thus, a conservative approach is generally preferred. The etiology is poorly understood, but there are ongoing efforts to better characterize FMD and define its genetic and molecular basis. This report reviews the clinical course of FMD involving the coronary arteries and provides guidance for diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; coronary vessel anomalies; fibromuscular dysplasia; left ventricular dysfunction; myocardial infarction.
Copyright © 2014 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Slovut D, Olin J. Fibromuscular dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1862–1871. - PubMed
-
- Olin JW, Froehlich J, Gu X, et al. The United States Registry for Fibromuscular Dysplasia: results in the first 447 patients. Circulation. 2012;125:3182–3190. - PubMed
-
- Olin JW, Sealove BA. Diagnosis, management, and future developments of fibromuscular dysplasia. J Vase Surg. 2011;53:826–836. - PubMed
-
- Touze E, Oppenheim C, Trystram D, et al. Fibromuscular dysplasia of cervical and intracranial arteries. Int J Stroke. 2010;5:296–305. - PubMed
-
- Saw J, Ricci D, Starovoytov A, et al. Spontaneous coronary artery dissection: prevalence of predisposing conditions including fibromuscular dysplasia in a tertiary center cohort. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2013;6:44–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

