Root canal therapy reduces multiple dimensions of pain: a national dental practice-based research network study
- PMID: 25190605
- PMCID: PMC4254176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.07.011
Root canal therapy reduces multiple dimensions of pain: a national dental practice-based research network study
Abstract
Introduction: Initial orthograde root canal therapy (RCT) is used to treat dentoalveolar pathosis. The effect RCT has on pain intensity has been frequently reported, but the effect on other dimensions of pain has not. Also, the lack of large prospective studies involving diverse groups of patients and practitioners who are not involved in data collection suggest that there are multiple opportunities for bias to be introduced when these data are systematically aggregated.
Methods: This prospective observational study assessed pain intensity, duration, and its interference with daily activities among RCT patients. Sixty-two practitioners (46 general dentists and 16 endodontists) in the National Dental Practice-Based Research Network enrolled patients requiring RCT. Patient-reported data were collected before, immediately after, and 1 week after treatment using the Graded Chronic Pain Scale.
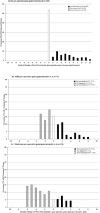
Results: The enrollment of 708 patients was completed over 6 months with 655 patients (93%) providing 1-week follow-up data. Before treatment, patients reported a mean (± standard deviation) worst pain intensity of 5.3 ± 3.8 (0-10 scale), 50% had "severe" pain (≥ 7), and mean days in pain and days pain interfered with activities were 3.6 ± 2.7 and 0.5 ± 1.2, respectively. After treatment, patients reported a mean worst pain intensity of 3.0 ± 3.2, 19% had "severe" pain, and mean days in pain and days with pain interference were 2.1 ± 2.4 and 0.4 ± 1.1, respectively. All changes were statistically significant (P < .0001).
Conclusions: RCT is an effective treatment for patients experiencing pain, significantly reducing pain intensity, duration, and related interference. Further research is needed to reduce the proportion of patients experiencing "severe" postoperative pain.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01201681.
Keywords: Endodontics; evidence-based dentistry; pain; pain measurement; postoperative pain; quality of care; research; root canal.
Copyright © 2014 American Association of Endodontists. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- American Dental Association Survey Center. 2005-06 survey of dental services rendered. Chicago: American Dental Association; 2007.
-
- Wolcott J, Rossman LE, Hasselgren G. Management of endodontic emergencies. In: Hargreaves KM, Cohen S, editors. Cohen's pathways of the pulp. 10th. St Louis: Mosby Elsevier; 2011. pp. 40–8.
-
- Kojima K, Inamoto K, Nagamatsu K, Hara A, Nakata K, Morita I, et al. Success rate of endodontic treatment of teeth with vital and nonvital pulps. A meta-analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004 Jan;97(1):95–9. - PubMed
-
- Ng YL, Mann V, Gulabivala K. A prospective study of the factors affecting outcomes of nonsurgical root canal treatment: Part 1: Periapical health. Int Endod J. 2011 Jul;44(7):583–609. - PubMed
-
- Sathorn C, Parashos P, Messer H. The prevalence of postoperative pain and flare-up in single-and multiple-visit endodontic treatment: A systematic review. Int Endod J. 2008 Feb;41(2):91–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical