Crystalglobulin-induced nephropathy
- PMID: 25190731
- PMCID: PMC4341488
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2014050509
Crystalglobulin-induced nephropathy
Abstract
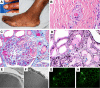
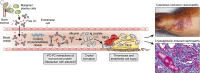
Crystalline nephropathy refers to renal parenchymal deposition of crystals leading to kidney damage. The most common forms of crystalline nephropathy encountered in renal pathology are nephrocalcinosis and oxalate nephropathy. Less frequent types include urate nephropathy, cystinosis, dihydroxyadeninuria, and drug-induced crystalline nephropathy (e.g., caused by indinavir or triamterene). Monoclonal proteins can also deposit in the kidney as crystals and cause tissue damage. This occurs in conditions such as light chain proximal tubulopathy, crystal-storing histiocytosis, and crystalglobulinemia. The latter is a rare complication of multiple myeloma that results from crystallization of monoclonal proteins in the systemic vasculature, leading to vascular injury, thrombosis, and occlusion. In this report, we describe a case of crystalglobulin-induced nephropathy and discuss its pathophysiology and the differential diagnosis of paraprotein-induced crystalline nephropathy.
Keywords: ARF; kidney biopsy; myeloma.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Nasr SH, Valeri AM, Sethi S, Fidler ME, Cornell LD, Gertz MA, Lacy M, Dispenzieri A, Rajkumar SV, Kyle RA, Leung N: Clinicopathologic correlations in multiple myeloma: A case series of 190 patients with kidney biopsies. Am J Kidney Dis 59: 786–794, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Ball NJ, Wickert W, Marx LH, Thaell JF: Crystalglobulinemia syndrome. A manifestation of multiple myeloma. Cancer 71: 1231–1234, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Dornan TL, Blundell JW, Morgan AG, Burden RP, Reeves WG, Cotton RE: Widespread crystallisation of paraprotein in myelomatosis. Q J Med 57: 659–667, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto R, Toda T, Tsutsumi H, Ohta M, Mori M: Abnormal N-glycosylation of the immunoglobulin G kappa chain in a multiple myeloma patient with crystalglobulinemia: Case report. Int J Hematol 85: 203–206, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Stone GC, Wall BA, Oppliger IR, Wener MH, Jolly SL, Aguirre A, Dwyer R, Simkin PA: A vasculopathy with deposition of lambda light chain crystals. Ann Intern Med 110: 275–278, 1989 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

