Driving toward targeted therapy for LCH
- PMID: 25190750
- PMCID: PMC4155264
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-587378
Driving toward targeted therapy for LCH
Abstract
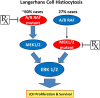
In this issue of Blood, Brown et al identify somatic mutations of MAP2K1 capable of driving the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH). Their findings lend important insight into the pathogenesis of this disease and provide the rationale for exploring targeted approaches in clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author declares no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment on
-
High prevalence of somatic MAP2K1 mutations in BRAF V600E-negative Langerhans cell histiocytosis.Blood. 2014 Sep 4;124(10):1655-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-577361. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24982505
References
-
- Brown NA, Furtado LV, Betz BL, et al. High prevalence of somatic MAP2K1 mutations in BRAF V600E negative Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2014;124(10):1655–1658. - PubMed
-
- Delprat C, Aricò M. Blood spotlight on Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2014;124(6):867–872. - PubMed
-
- Haroche J, Cohen-Aubart F, Emile JF, et al. Dramatic efficacy of vemurafenib in both multisystemic and refractory Erdheim-Chester disease and Langerhans cell histiocytosis harboring the BRAF V600E mutation. Blood. 2013;121(9):1495–1500. - PubMed
-
- Nelson DS, Quispel W, Badalian-Very G, et al. Somatic activating ARAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2014;123(20):3152–3155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

