Characteristics of mobile MOSFET dosimetry system for megavoltage photon beams
- PMID: 25190992
- PMCID: PMC4154181
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6203.139002
Characteristics of mobile MOSFET dosimetry system for megavoltage photon beams
Abstract
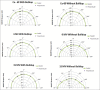
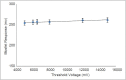
The characteristics of a mobile metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (mobile MOSFET) detector for standard bias were investigated for megavoltage photon beams. This study was performed with a brass alloy build-up cap for three energies namely Co-60, 6 and 15 MV photon beams. The MOSFETs were calibrated and the performance characteristics were analyzed with respect to dose rate dependence, energy dependence, field size dependence, linearity, build-up factor, and angular dependence for all the three energies. A linear dose-response curve was noted for Co-60, 6 MV, and 15 MV photons. The calibration factors were found to be 1.03, 1, and 0.79 cGy/mV for Co-60, 6 MV, and 15 MV photon energies, respectively. The calibration graph has been obtained to the dose up to 600 cGy, and the dose-response curve was found to be linear. The MOSFETs were found to be energy independent both for measurements performed at depth as well as on the surface with build-up. However, field size dependence was also analyzed for variable field sizes and found to be field size independent. Angular dependence was analyzed by keeping the MOSFET dosimeter in parallel and perpendicular orientation to the angle of incidence of the radiation with and without build-up on the surface of the phantom. The maximum variation for the three energies was found to be within ± 2% for the gantry angles 90° and 270°, the deviations without the build-up for the same gantry angles were found to be 6%, 25%, and 60%, respectively. The MOSFET response was found to be independent of dose rate for all three energies. The dosimetric characteristics of the MOSFET detector make it a suitable in vivo dosimeter for megavoltage photon beams.
Keywords: Angular dependence; build-up; dose rate; dosimetry; field size dependence; linearity; metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor; threshold voltage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Marcié S, Charpiot E, Bensadoun RJ, Ciais G, Hérault J, Costa A, et al. In vivo measurements with MOSFET detectors in oropharynx and nasopharynx intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61:1603–6. - PubMed
-
- Beyer GP, Kry SF, Espenhahn E, Rini C, Boyles E, Mann G. Evaluation of an implantable MOSFET dosimeter designed for use with hypofractionated external beam treatments and its applications for breast and prostate treatments. Med Phys. 2011;38:4881–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

