Complement, c1q, and c1q-related molecules regulate macrophage polarization
- PMID: 25191325
- PMCID: PMC4139736
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00402
Complement, c1q, and c1q-related molecules regulate macrophage polarization
Abstract
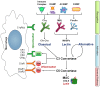
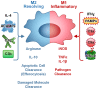
Complement is a critical system of enzymes, regulatory proteins, and receptors that regulates both innate and adaptive immune responses. Natural mutations in complement molecules highlight their requirement in regulation of a variety of human conditions including infectious disease and autoimmunity. As sentinels of the immune system, macrophages are specialized to respond to infectious microbes, as well as normal and altered self, and dictate appropriate immune responses. Complement components such as anaphylatoxins (C3a and C5a) and opsonins [C3b, C1q, mannan binding lectin (MBL)] influence macrophage responses. While anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a trigger inflammasome activation, opsonins such as C1q and related molecules (MBL and adiponectin) downregulate inflammasome activation and inflammation, and upregulate engulfment of apoptotic cells consistent with a pro-resolving or M2 macrophage phenotype. This review summarizes our current understanding of the influence of the complement system on macrophage polarization with an emphasis on C1q and related molecules.
Keywords: C1q; adiponectin; complement; cytokine; efferocytosis; inflammasome; macrophage; phagocytosis.
Figures
References
-
- Jiang H, Burdick D, Glabe CG, Cotman CW, Tenner AJ. Beta-amyloid activates complement by binding to a specific region of the collagen-like domain of the C1q A chain. J Immunol (1994) 152(10):5050–9 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

